Managing Eczema: A Guide to Effective Products and Practices
Related Articles: Managing Eczema: A Guide to Effective Products and Practices
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Managing Eczema: A Guide to Effective Products and Practices. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Managing Eczema: A Guide to Effective Products and Practices

Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. It manifests as itchy, red, and inflamed patches of skin, often accompanied by dryness, scaling, and cracking. While there is no cure for eczema, effective management strategies exist, including the use of topical treatments, moisturizers, and other products that help alleviate symptoms and improve skin health. This article provides a comprehensive overview of products that can be beneficial for managing eczema, offering insights into their mechanisms of action, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Topical Treatments: The Cornerstone of Eczema Management
Topical treatments are applied directly to the skin and are considered the mainstay of eczema management. They work by reducing inflammation, itching, and dryness, thereby improving the appearance and feel of the skin.
-
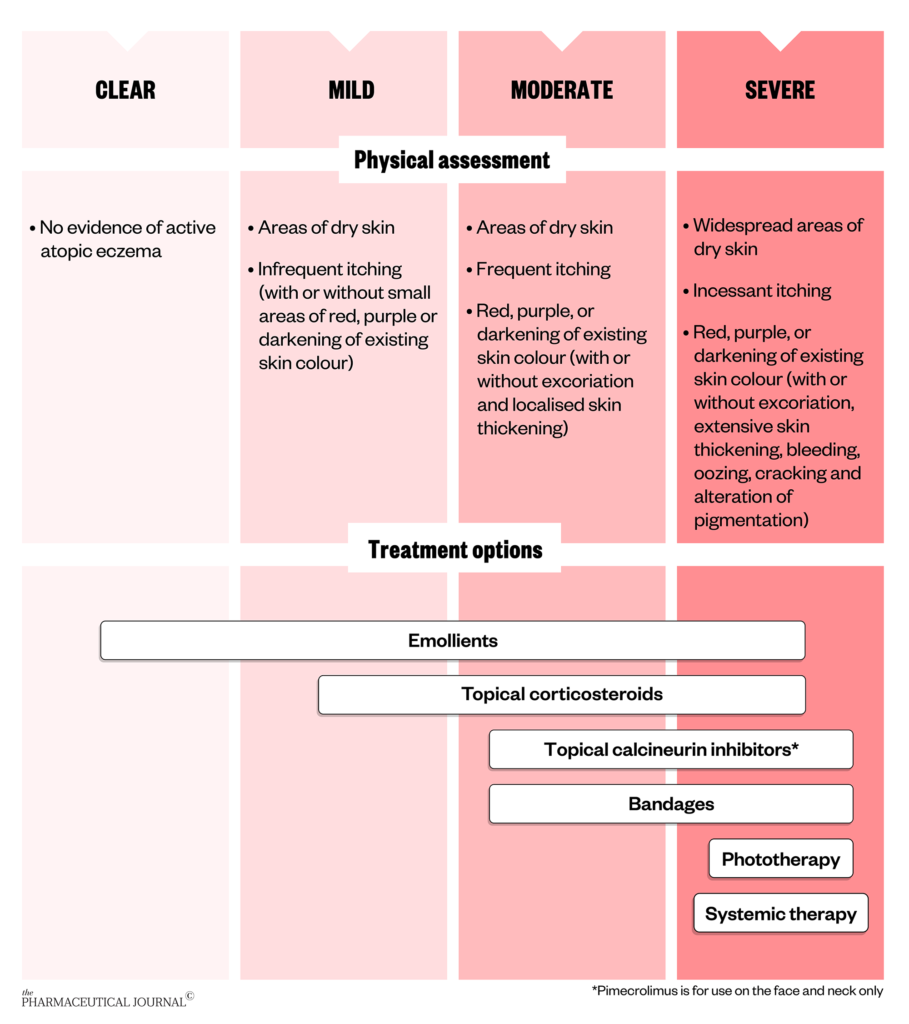
Corticosteroids: These are potent anti-inflammatory medications that effectively reduce redness, swelling, and itching. They are available in various strengths and forms, including creams, ointments, lotions, and gels. While highly effective, prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to skin thinning and other side effects, making it crucial to use them as directed by a dermatologist.
-
Calcineurin Inhibitors: These medications, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, suppress the immune response that triggers eczema flares. They are often used for chronic eczema, particularly on sensitive areas like the face and eyelids, as they carry a lower risk of side effects compared to corticosteroids. However, they can still cause skin irritation and should be used cautiously.
-
Antihistamines: While not directly targeting eczema, antihistamines can alleviate itching, a significant symptom associated with the condition. Oral antihistamines, such as cetirizine and loratadine, can be helpful for managing generalized itching, while topical antihistamines, like diphenhydramine cream, can target specific areas.
Moisturizers: The Foundation for Healthy Skin
Moisturizers are essential for eczema management, as they help restore the skin’s natural barrier, prevent dryness, and reduce itching.
-
Emollients: These are moisturizing agents that soften and smooth the skin. They work by trapping moisture within the skin, improving hydration and reducing dryness. Emollients come in various forms, including creams, lotions, and ointments, each with a different consistency and absorption rate.
-
Humectants: These ingredients draw moisture from the air and bind it to the skin, increasing hydration levels. Common humectants include hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and urea.
-
Occlusives: These ingredients create a barrier on the skin’s surface, preventing moisture loss and enhancing hydration. Petroleum jelly, lanolin, and dimethicone are examples of occlusives.
Other Products for Eczema Management
Beyond topical treatments and moisturizers, other products can complement eczema management strategies.
-
Antiseptics: These agents help prevent bacterial and fungal infections, which can worsen eczema symptoms. Common antiseptics include benzoyl peroxide, chlorhexidine, and iodine.
-
Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection develops, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and prevent further complications.
-
Phototherapy: This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet light, which can reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response.
-
Wet Wraps: This technique involves applying a wet compress to the affected skin, followed by a layer of moisturizer and an occlusive dressing. Wet wraps can effectively hydrate the skin, reduce itching, and promote healing.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Eczema Products
Q: What are the safest and most effective eczema products for babies and children?
A: For babies and children, gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers are crucial. Emollients like petroleum jelly and mineral oil can be effective, while topical corticosteroids should be used cautiously and only under a dermatologist’s guidance.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for eczema?
A: Some natural remedies, like oatmeal baths and applying aloe vera gel, can provide temporary relief from itching and dryness. However, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist before using any natural remedies, as some may trigger allergic reactions or interact with other medications.
Q: How can I prevent eczema flare-ups?
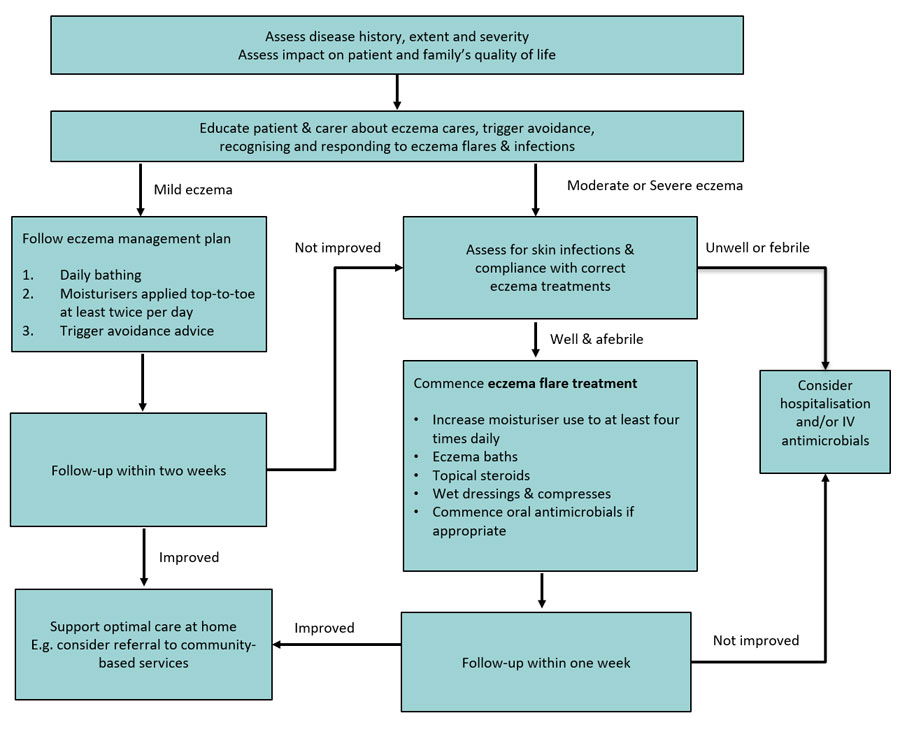
A: Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial. Common triggers include allergens like dust mites, pollen, and pet dander, irritants like harsh soaps and detergents, and stress. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, including daily moisturizing, can also help prevent flare-ups.
Tips for Effective Eczema Management
-
Consult a dermatologist: A dermatologist can provide personalized advice and recommend the most appropriate products for your specific needs.
-
Follow a consistent skincare routine: Regular moisturizing is crucial, even during symptom-free periods.
-
Avoid harsh soaps and detergents: Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products.
-
Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing: Avoid fabrics that irritate the skin, such as wool and synthetic materials.
-
Keep nails trimmed: Scratching can worsen eczema symptoms and increase the risk of infection.
-
Identify and avoid triggers: Keep a diary to track potential triggers and adjust your lifestyle accordingly.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals to Manage Eczema Effectively
Eczema is a complex condition that can significantly impact quality of life. However, with proper management, individuals can effectively control symptoms and improve their overall well-being. By understanding the various products available, their mechanisms of action, and potential benefits and drawbacks, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized management plan. This plan should include a combination of topical treatments, moisturizers, and other products tailored to individual needs, alongside lifestyle modifications to minimize triggers and promote healthy skin.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Eczema: A Guide to Effective Products and Practices. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!