Restoring Skin and Healing Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Practices
Related Articles: Restoring Skin and Healing Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Practices
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Restoring Skin and Healing Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Practices. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Restoring Skin and Healing Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Practices
The human skin is a remarkable organ, acting as a barrier against the environment while also serving as a crucial component of our immune system. However, it is susceptible to damage from various sources, including injuries, infections, and chronic conditions. This damage can manifest in the form of wounds, burns, ulcers, and other skin conditions, requiring specialized care to facilitate healing and restore skin integrity.
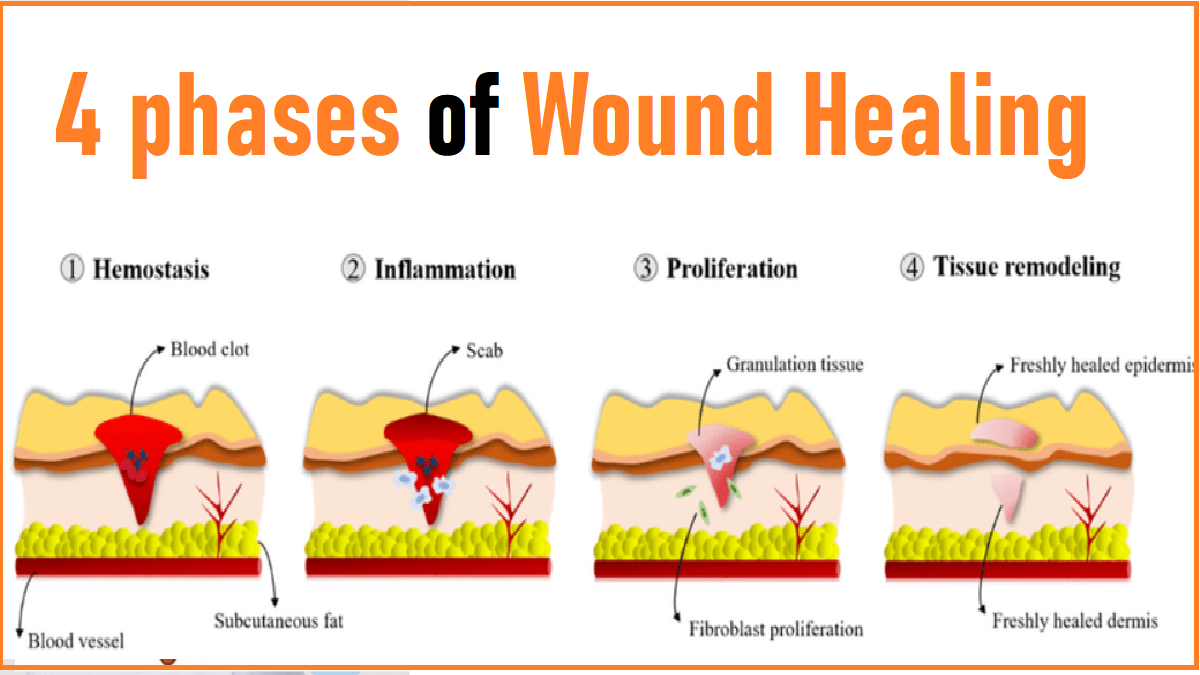
Understanding Wound Healing and Skin Repair
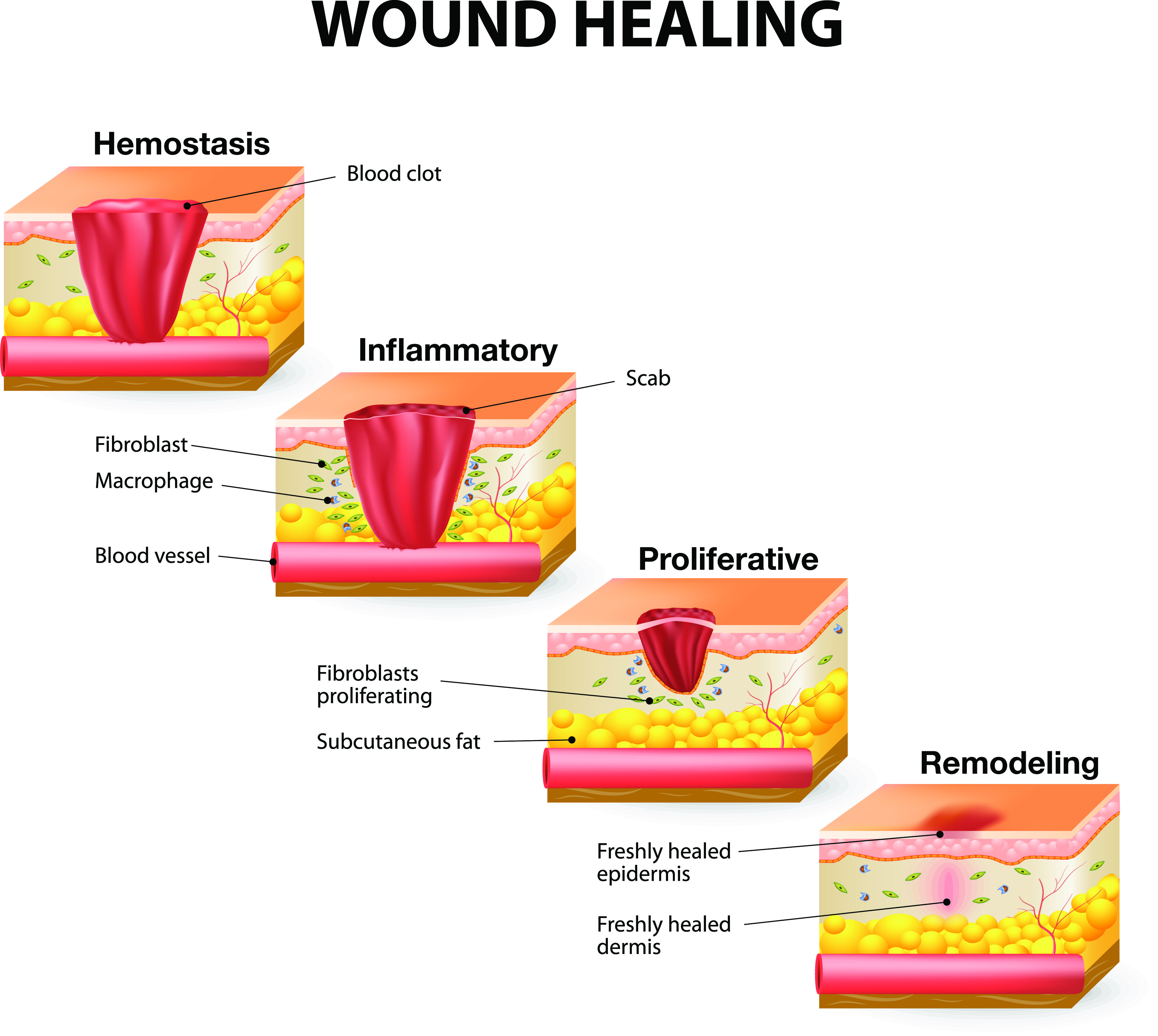
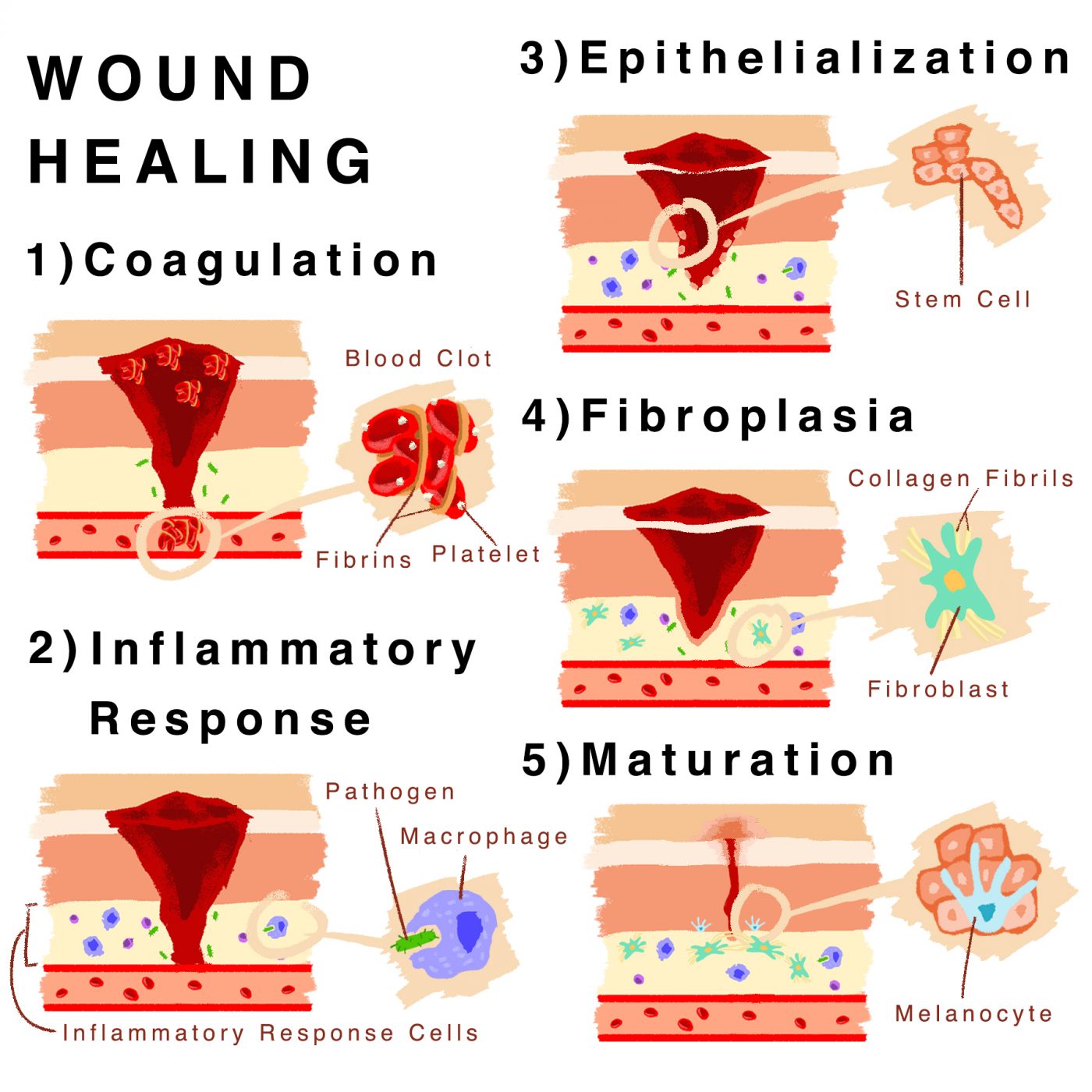
The process of wound healing is a complex interplay of biological mechanisms, involving multiple stages:
- Hemostasis: The initial response to injury, involving blood clotting to stop bleeding and form a protective barrier.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response, characterized by the recruitment of immune cells to the wound site to clear debris and fight infection.
- Proliferation: The formation of new tissue, including granulation tissue, to fill the wound space.
- Remodeling: The final stage, where the new tissue matures and strengthens, resulting in scar formation.
Skin repair mechanisms are similar, aiming to restore the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (inner layer) to their original structure and function. This involves cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, and the formation of new blood vessels.
The Role of Wound and Skin Care Products
Specialized products play a critical role in supporting these natural healing processes, promoting faster and healthier wound closure, and minimizing the risk of complications. These products can be broadly categorized as:
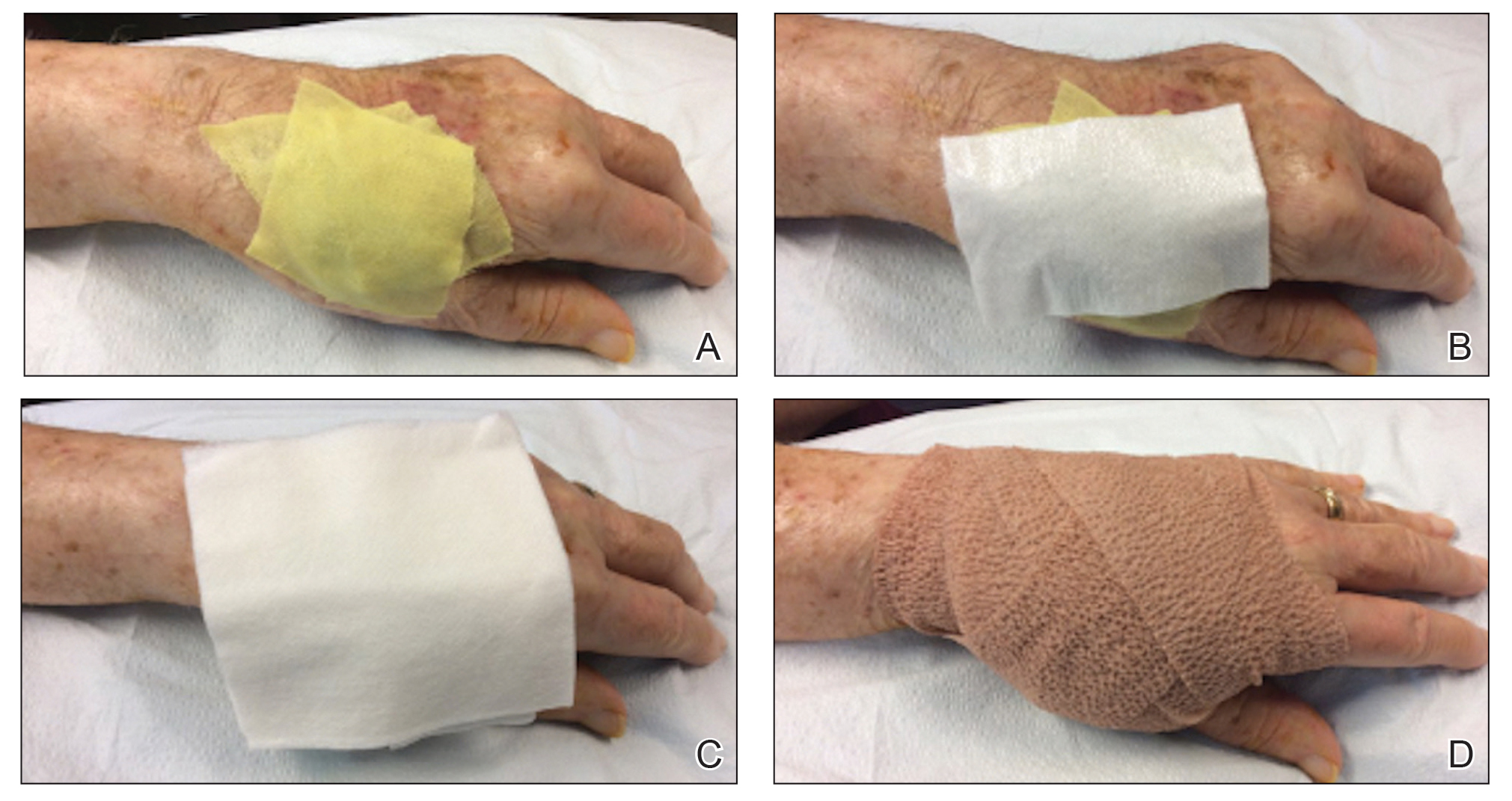
1. Wound Dressings:
These are applied directly to the wound to provide a protective barrier, absorb exudate (wound drainage), and promote healing. Different types of dressings are available, tailored to specific wound types and stages of healing:
- Hydrocolloid dressings: These create a moist environment, promoting autolytic debridement (the removal of dead tissue by the body’s own enzymes). They are often used for minor wounds, burns, and ulcers.
- Hydrogel dressings: These are gel-like dressings that hydrate the wound and promote granulation tissue formation. They are suitable for dry wounds and burns.
- Alginate dressings: These are made from seaweed and are highly absorbent, ideal for wounds with heavy exudate.
- Foam dressings: These provide cushioning and absorption, suitable for moderate to heavily draining wounds.
- Transparent film dressings: These provide a barrier against bacteria and moisture while allowing visualization of the wound. They are commonly used for superficial wounds and burns.
2. Topical Antiseptics and Antimicrobials:
These products are used to prevent and treat infections, reducing the risk of wound contamination and delaying healing. Common examples include:
- Povidone-iodine: A broad-spectrum antiseptic that kills bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Chlorhexidine: Another broad-spectrum antiseptic with persistent antimicrobial activity.
- Silver sulfadiazine: An antimicrobial cream used to treat burns and other wounds.
3. Skin Protectants and Moisturizers:
These products help to maintain skin hydration, prevent dryness, and support the skin’s barrier function, particularly crucial for individuals with sensitive skin or those undergoing treatment for skin conditions.
- Emollients: These are moisturizing agents that help to soften and smooth the skin.
- Humectants: These attract and retain moisture in the skin.
- Occlusives: These create a barrier on the skin, preventing moisture loss.
4. Skin Repairing Agents:
These products contain ingredients that stimulate the skin’s natural healing processes, promoting cell regeneration and collagen synthesis. Common examples include:
- Growth factors: These proteins promote cell division and proliferation, accelerating wound healing.
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives increase collagen production and improve skin texture.
- Hyaluronic acid: This natural substance attracts and retains moisture, promoting skin hydration and elasticity.
5. Wound Closure Devices:
These devices are used to close wounds, minimizing scarring and reducing the risk of infection. Examples include:
- Sutures: These are threads used to close wounds surgically.
- Staples: These are metal clips used to close wounds.
- Adhesive strips: These are strips used to close minor wounds.
Beyond Products: Essential Practices for Optimal Wound and Skin Care
While products play a significant role, proper wound and skin care practices are equally essential for successful healing:
- Gentle Cleansing: Regularly cleaning wounds with mild soap and water or saline solution removes debris and bacteria.
- Moisture Management: Maintaining a slightly moist environment promotes healing, while excessive moisture can increase infection risk.
- Protection: Protecting wounds from further injury and environmental factors is crucial.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamin C, and zinc supports wound healing.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining skin hydration and overall health.
- Rest: Allowing the body to rest and recover is crucial for optimal healing.
FAQs about Wound and Skin Care Products
1. What are the key considerations when choosing a wound dressing?
The selection of a wound dressing depends on several factors, including the type and size of the wound, the amount of exudate, the presence of infection, and the patient’s individual needs. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate dressing.
2. Are topical antiseptics always necessary for wound care?
While antiseptics can be beneficial in preventing infection, they should be used with caution, as some can damage healthy tissue. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and consult with a healthcare professional before using any topical antiseptics.
3. How often should I apply skin protectants and moisturizers?
The frequency of application depends on the specific product and the individual’s skin type. It is generally recommended to apply moisturizers twice daily, after bathing or showering.
4. Are skin repairing agents suitable for all skin types?
Skin repairing agents can be beneficial for various skin types, but it is essential to choose products formulated for specific skin concerns. Individuals with sensitive skin should consult with a dermatologist before using any new products.
5. When should I seek medical attention for a wound?
Seek immediate medical attention if a wound is deep, bleeding profusely, showing signs of infection (redness, swelling, pus), or if it is located on the face, hands, or feet.
Tips for Effective Wound and Skin Care
- Read product labels carefully: Understand the intended use, potential side effects, and application instructions before using any product.
- Follow instructions diligently: Proper application and usage are crucial for product efficacy and safety.
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Seek guidance from a doctor or nurse for specific wound and skin care needs.
- Keep wounds clean and dry: Regular cleansing and proper drying are essential to prevent infection.
- Protect wounds from further injury: Avoid rubbing or scratching the wound area.
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash hands frequently to prevent contamination.
- Monitor for signs of infection: Seek medical attention if you notice any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pus, or fever.
Conclusion
Wound and skin care products play a vital role in facilitating healing, promoting skin health, and improving quality of life. Understanding the different types of products available, their mechanisms of action, and proper application techniques is crucial for effective use. By combining appropriate product selection with good hygiene practices, individuals can optimize wound healing and maintain healthy skin, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting overall well-being.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Restoring Skin and Healing Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide to Products and Practices. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!