Skin Cancer in Washington State: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Skin Cancer in Washington State: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Skin Cancer in Washington State: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Skin Cancer in Washington State: A Comprehensive Overview
Skin cancer is a significant public health concern in Washington State, as it is in many parts of the world. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of skin cancer in the state, encompassing its prevalence, risk factors, prevention strategies, and the importance of early detection and treatment.
Prevalence and Incidence:
Washington State experiences a considerable burden of skin cancer, reflecting its geographic location and population demographics. The state’s diverse landscape, encompassing mountains, forests, and coastlines, exposes residents to varying levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Additionally, Washington’s climate, with extended periods of sunshine, further increases the risk of skin cancer development.
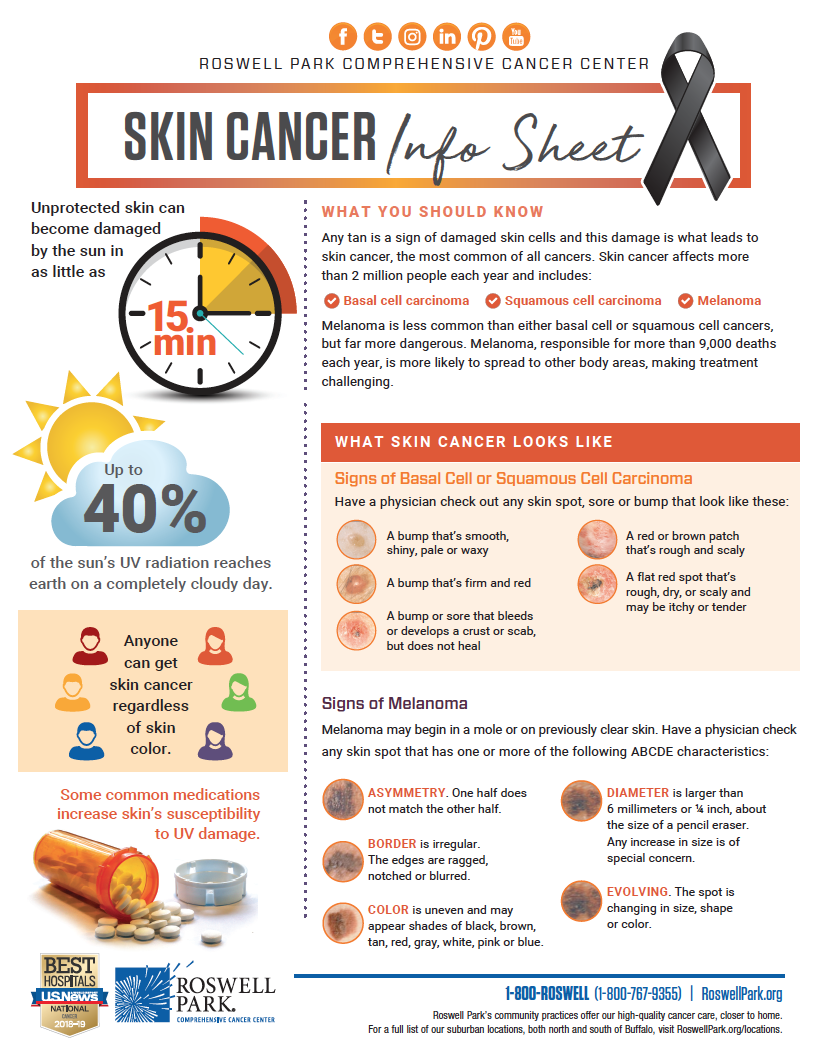
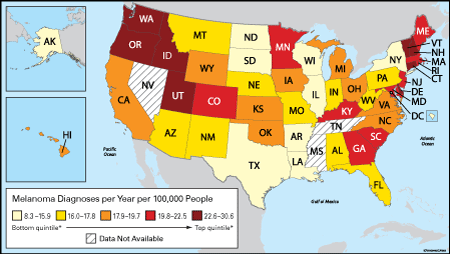
Data from the Washington State Department of Health (DOH) reveals a substantial incidence of skin cancer. In 2020, there were approximately 20,000 new cases of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, diagnosed in Washington. Non-melanoma skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, are even more prevalent, with an estimated 100,000 new cases diagnosed annually.
Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to the development of skin cancer, including:
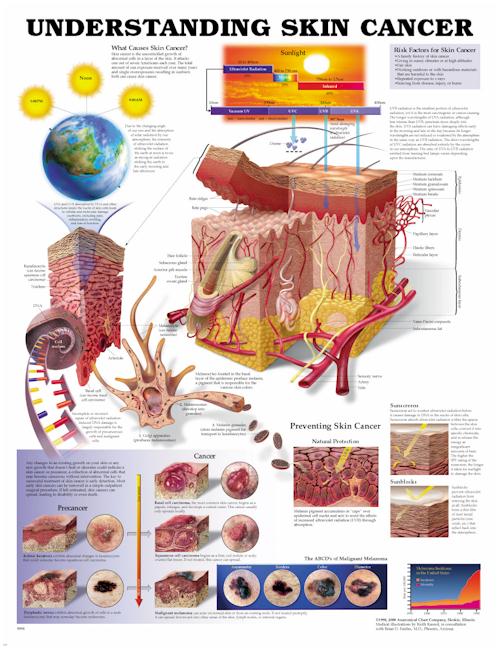
- Excessive Sun Exposure: Prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun’s UV radiation is the primary risk factor for skin cancer.
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin, freckles, and light hair are more susceptible to sun damage and skin cancer.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer significantly increases an individual’s risk.
- Age: Skin cancer incidence rises with age, as cumulative sun exposure over a lifetime takes its toll.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more vulnerable to skin cancer development.
- Artificial Tanning: Tanning beds and sunlamps emit UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Prevention Strategies:
Effective prevention strategies are crucial in mitigating the risk of skin cancer. These include:
- Sun Protection: Minimizing sun exposure during peak hours (10 am to 4 pm) and utilizing sun-protective measures like sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses is paramount.
- Sunscreen Application: Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher generously and frequently, especially during outdoor activities, is essential.
- Regular Skin Exams: Conducting regular self-exams to identify any suspicious moles or skin changes is crucial for early detection.
- Professional Skin Examinations: Seeking regular skin examinations from a dermatologist or healthcare provider is highly recommended, particularly for individuals at higher risk.
- Avoiding Tanning Beds: Tanning beds and sunlamps should be avoided altogether due to their proven link to skin cancer.
Early Detection and Treatment:
Early detection is key to successful skin cancer treatment. Regular skin exams by individuals and healthcare professionals are vital in identifying suspicious lesions.
Skin cancer treatment options vary depending on the type, stage, and location of the cancer. Common treatment methods include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous lesion is the most common treatment for skin cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs are used to target and kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection of skin cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. When detected in its early stages, skin cancer is highly treatable. However, as the cancer progresses, treatment becomes more complex and the chances of survival decrease.
FAQs:
Q: What are the warning signs of skin cancer?
A: Look for the following warning signs:
- Asymmetry: The mole or lesion is not symmetrical.
- Border Irregularity: The edges are irregular, blurred, or jagged.
- Color Variation: The mole has multiple colors, including shades of brown, black, red, or white.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolving: The mole changes in size, shape, or color.
Q: How often should I perform self-skin exams?
A: It is recommended to perform a full-body skin exam monthly. Pay close attention to areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, ears, arms, legs, and back.
Q: Who should I see for a skin cancer screening?
A: You should consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider for a professional skin cancer screening.
Q: Is skin cancer preventable?
A: While some risk factors for skin cancer are not preventable, such as genetics, many are modifiable. Following sun protection guidelines and avoiding tanning beds can significantly reduce your risk.
Q: What are the long-term effects of skin cancer treatment?
A: The long-term effects of skin cancer treatment vary depending on the type of treatment and the individual’s overall health. Some potential effects may include scarring, skin discoloration, and changes in sensation.
Tips:
- Protect your skin from the sun: Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, and apply sunscreen regularly.
- Perform regular self-skin exams: Be familiar with your skin and report any changes to your healthcare provider.
- See a dermatologist for regular skin screenings: Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps: These devices emit harmful UV radiation that increases your risk of skin cancer.
- Educate yourself and others about skin cancer: Spread awareness about prevention, detection, and treatment.
Conclusion:
Skin cancer is a serious public health concern in Washington State, but it is also largely preventable. By adopting sun-protective measures, performing regular skin exams, and seeking professional care, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this disease. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment and improved survival rates. By increasing awareness and promoting preventive measures, we can collectively strive to reduce the burden of skin cancer in our communities.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Skin Cancer in Washington State: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!