The Allure of "Second Skin": Exploring the World of Protective Films and Coatings
Related Articles: The Allure of "Second Skin": Exploring the World of Protective Films and Coatings
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Allure of "Second Skin": Exploring the World of Protective Films and Coatings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Allure of "Second Skin": Exploring the World of Protective Films and Coatings

In the realm of modern materials science, the concept of a "second skin" has emerged as a powerful paradigm, encompassing a diverse range of protective films and coatings designed to enhance the durability, longevity, and functionality of various surfaces. This article delves into the fascinating world of "second skin" technologies, exploring their underlying principles, diverse applications, and the remarkable benefits they offer.
Understanding the Essence of "Second Skin"
The term "second skin" evokes a sense of seamless integration, a protective layer that seamlessly blends with the underlying substrate, offering an invisible shield against external threats. This analogy aptly captures the essence of these advanced materials, which are meticulously engineered to adhere tightly to surfaces, creating a robust barrier that safeguards against wear and tear, corrosion, chemical attack, and environmental degradation.
The Science Behind "Second Skin" Technologies
The development of "second skin" technologies relies on a sophisticated understanding of surface chemistry, polymer science, and materials engineering. These protective layers are typically composed of polymers, ceramics, or metallic alloys, carefully selected and formulated to provide specific properties tailored to the intended application.
Key Types of "Second Skin" Technologies
-
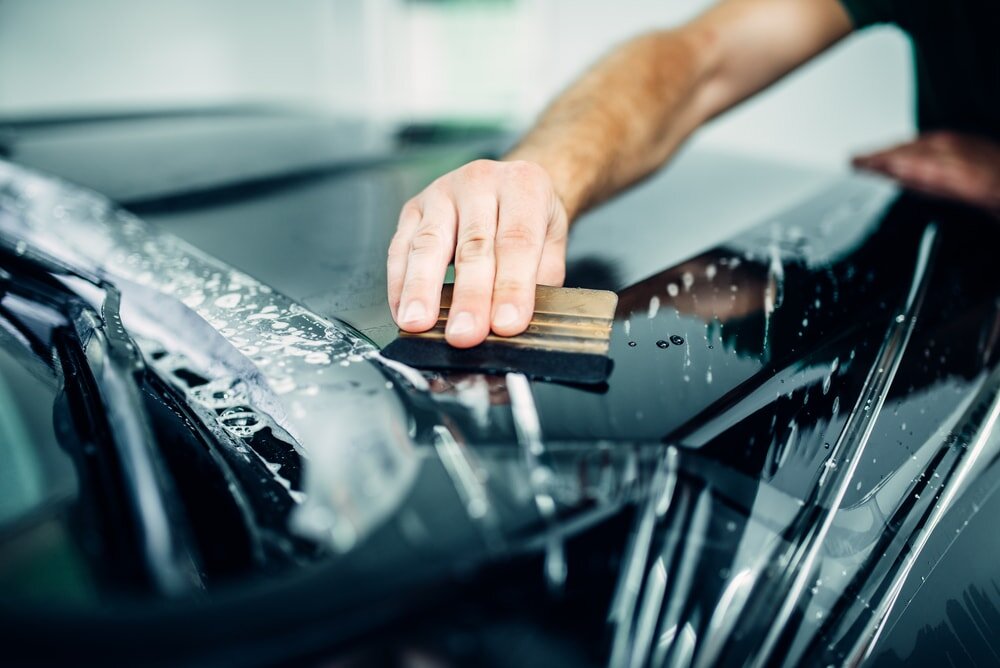
Protective Films: These thin, flexible layers are commonly used to safeguard surfaces against scratches, abrasions, and other forms of physical damage. Examples include:
- Screen Protectors: Applied to smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices to prevent scratches and cracks on the display.
- Paint Protection Films (PPF): Transparent, self-healing films that shield automotive paintwork from stone chips, scratches, and UV degradation.
- Anti-Glare Films: Applied to windows and screens to reduce glare and improve visual comfort.
-
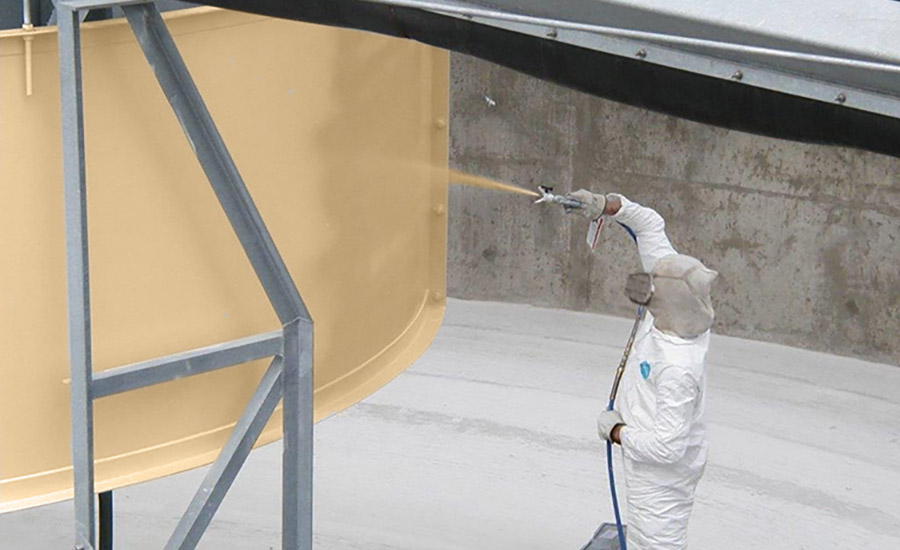
Coatings: These thicker, more robust layers are designed to provide enhanced protection against corrosion, chemical attack, and high temperatures. Examples include:
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Applied to metal surfaces to prevent rust and oxidation.
- Fire Retardant Coatings: Applied to building materials and other structures to reduce fire hazards.
- Thermal Barrier Coatings: Used in high-temperature applications to protect components from heat damage.
-
Nanocoatings: These ultra-thin coatings, often composed of nanomaterials, offer exceptional protection and functionality. Examples include:
- Water-Repellent Coatings: Applied to fabrics and surfaces to repel water and prevent staining.
- Anti-Bacterial Coatings: Applied to medical devices and surfaces to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Self-Cleaning Coatings: Applied to surfaces to facilitate the removal of dirt and grime.
The Benefits of "Second Skin" Technologies
The implementation of "second skin" technologies brings a multitude of benefits, enhancing the performance, longevity, and aesthetics of various products and structures.
- Enhanced Durability: These protective layers significantly improve the resistance of surfaces to wear and tear, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
- Corrosion Prevention: Coatings provide a robust barrier against corrosive environments, safeguarding metal components from rust and degradation.
- Chemical Resistance: "Second skin" technologies can be formulated to withstand specific chemical attacks, protecting surfaces from harsh environments.
- Improved Aesthetics: Protective films and coatings can enhance the appearance of surfaces, providing a glossy finish, restoring faded colors, or adding decorative elements.
- Increased Functionality: Nanocoatings can impart specialized functionalities, such as water repellency, self-cleaning properties, or anti-bacterial resistance.
Applications of "Second Skin" Technologies
The applications of "second skin" technologies are vast and diverse, extending across numerous industries and sectors.
- Automotive Industry: Paint protection films, anti-corrosion coatings, and scratch-resistant coatings are widely used in automotive manufacturing and aftermarket applications.
- Electronics Industry: Screen protectors, anti-static coatings, and thermal barrier coatings are essential for protecting delicate electronic components.
- Construction Industry: Fire retardant coatings, waterproofing membranes, and anti-graffiti coatings enhance the safety and durability of buildings and structures.
- Aerospace Industry: High-temperature coatings, anti-corrosion coatings, and wear-resistant coatings are crucial for protecting aircraft components from extreme conditions.
- Medical Industry: Anti-bacterial coatings, biocompatible coatings, and wear-resistant coatings are used in medical devices and implants.
FAQs Regarding "Second Skin" Technologies
1. How long do "second skin" technologies last?
The lifespan of "second skin" technologies varies significantly depending on the specific material, application, and environmental conditions. Some protective films may last for several years, while coatings can provide protection for decades.
2. Are "second skin" technologies environmentally friendly?
Many "second skin" technologies are environmentally friendly, using non-toxic materials and sustainable manufacturing processes. However, it is essential to research the specific environmental impact of each product before making a purchase.
3. How are "second skin" technologies applied?
The application process varies depending on the type of technology. Some films can be applied using a simple wet application method, while others require specialized equipment and techniques.
4. Are "second skin" technologies expensive?
The cost of "second skin" technologies can vary widely depending on the type of material, application, and complexity of the project. However, the long-term benefits of these technologies, such as reduced maintenance costs and extended lifespan, often outweigh the initial investment.
Tips for Choosing the Right "Second Skin" Technology
- Identify the Specific Needs: Clearly define the type of protection required, including the anticipated threats and environmental conditions.
- Research Different Options: Explore the various types of "second skin" technologies available, considering their properties, durability, and compatibility with the intended substrate.
- Consult with Experts: Seek advice from professionals in the field, such as coating specialists or materials engineers, to ensure the selection of the most appropriate technology for your application.
- Consider Long-Term Benefits: Evaluate the long-term benefits of "second skin" technologies, including reduced maintenance costs, extended lifespan, and improved performance.
Conclusion
"Second Skin" technologies have revolutionized the way we protect and enhance the performance of surfaces, offering a remarkable range of benefits across diverse industries and applications. From protecting delicate electronic devices to safeguarding critical infrastructure, these advanced materials play a vital role in our modern world, enhancing durability, extending lifespan, and improving functionality. As research and innovation continue to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated "second skin" technologies to emerge, further pushing the boundaries of materials science and shaping the future of our built environment.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Allure of "Second Skin": Exploring the World of Protective Films and Coatings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!