The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview
- 3.1 Skin Cancer: A Multifaceted Threat
- 3.2 Cosmetics: A Double-Edged Sword
- 3.3 Navigating the Complex Landscape: Key Considerations
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.5 Tips for Safe and Informed Cosmetic Use
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Skin Health
- 4 Closure
The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview

Skin cancer, a prevalent and potentially life-threatening disease, is a significant public health concern. Its development is intricately linked to various factors, including sun exposure, genetic predisposition, and lifestyle choices. Cosmetics, as products designed to enhance or alter the appearance of the skin, play a multifaceted role in this intricate equation. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for informed decision-making regarding skincare practices and the potential impact on skin health.
Skin Cancer: A Multifaceted Threat
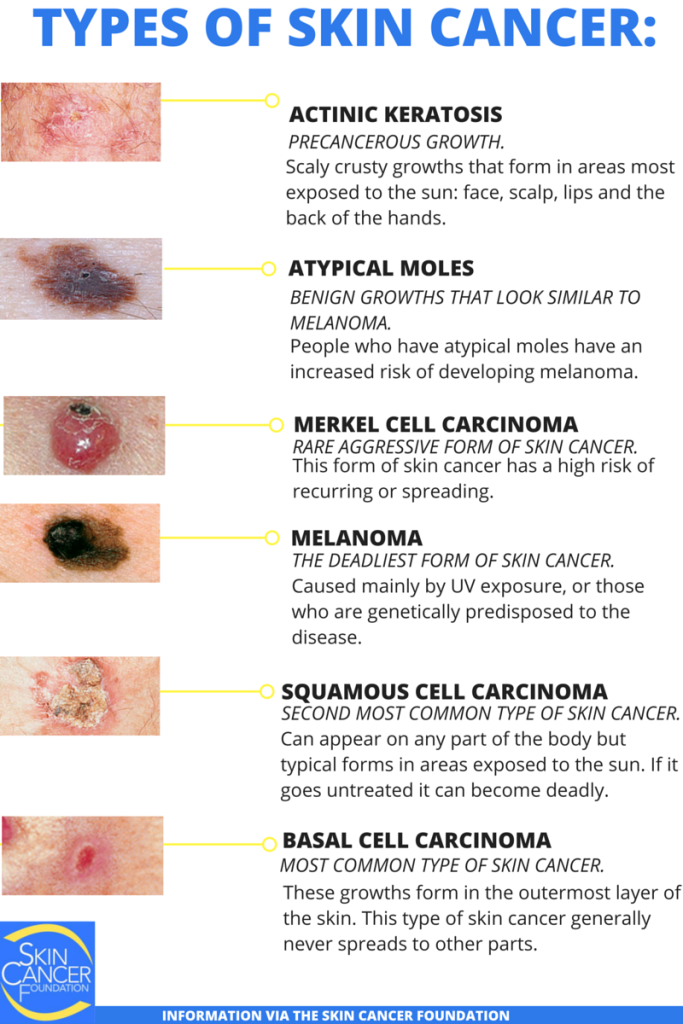
Skin cancer encompasses a spectrum of malignancies arising from the skin’s cells. The most common forms include:
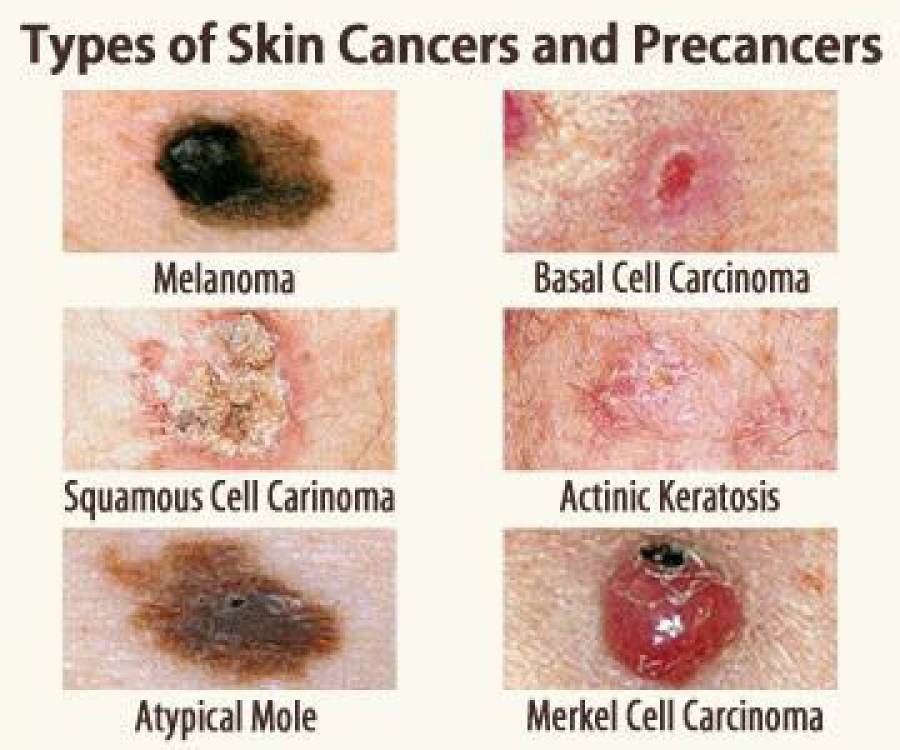
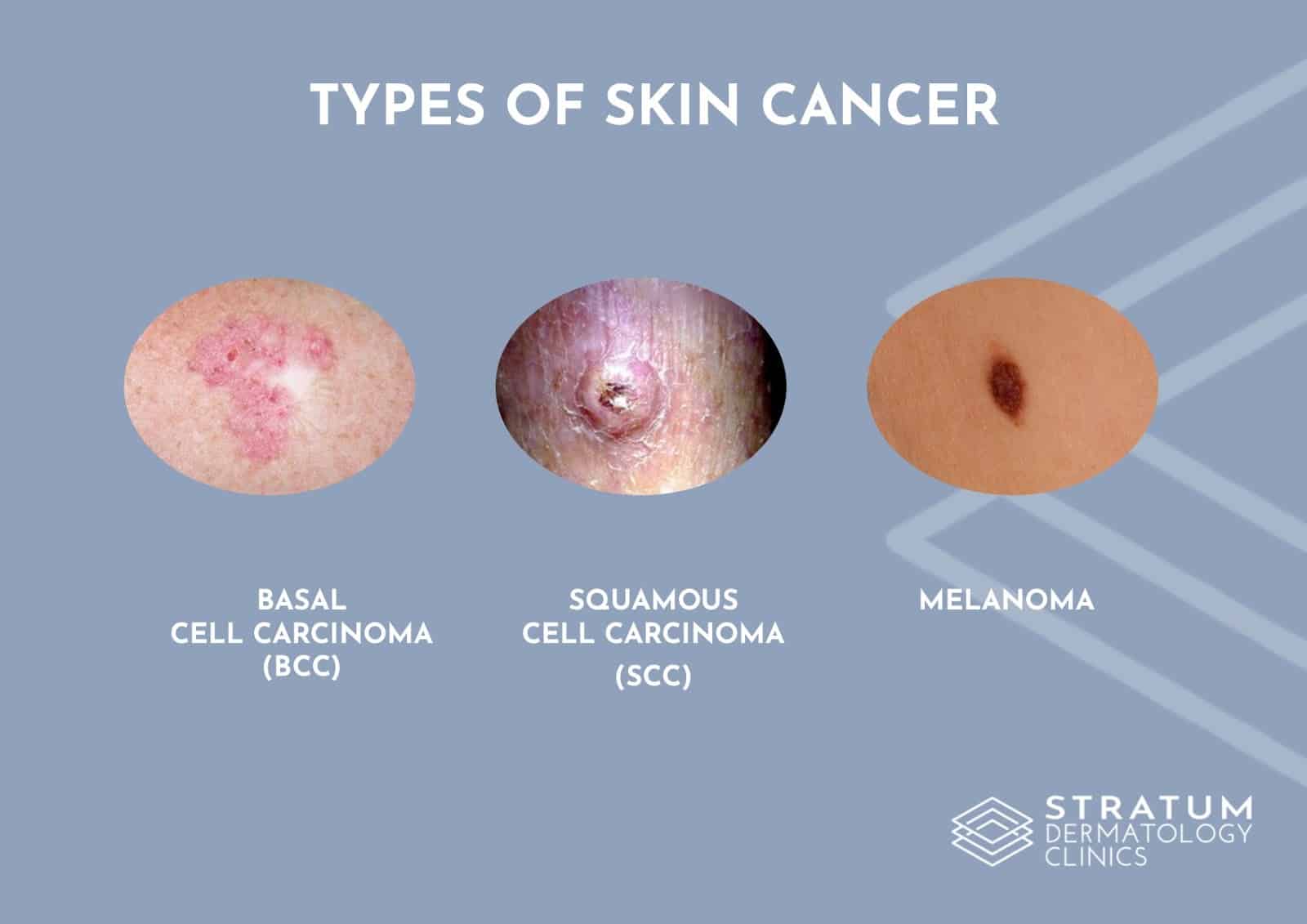
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most prevalent type, BCC typically arises from the basal cells in the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. It usually appears as pearly or waxy nodules and rarely metastasizes.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Originating from the squamous cells in the epidermis, SCC manifests as firm, red nodules or scaly patches. While less common than BCC, SCC has a higher risk of metastasis.
- Melanoma: The most aggressive and potentially deadly form of skin cancer, melanoma develops from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. It can present in various forms, including moles, freckles, or discolored patches.
While the precise causes of skin cancer remain complex, several key risk factors contribute to its development:
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds is a primary driver of skin cancer. UV rays damage DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can trigger uncontrolled growth.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Individuals with a family history of the disease or specific genetic syndromes are more susceptible.
- Fair Skin and Light Hair: People with fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes have less melanin, the pigment that protects the skin from UV radiation. This makes them more vulnerable to sun damage and subsequent cancer development.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as cumulative sun exposure and cellular damage accumulate over time.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and weakened immune systems can also increase the risk of skin cancer.
Cosmetics: A Double-Edged Sword
Cosmetics, while often associated with enhancing beauty, can also pose potential risks to skin health, including contributing to skin cancer development. This complexity arises from the diverse range of ingredients and formulations found in cosmetic products.
Potential Benefits:
- Sun Protection: Some cosmetics contain sunscreen ingredients, offering protection against UV radiation and reducing the risk of sun-induced skin cancer.
- Skin Care: Certain cosmetic ingredients can promote skin health by hydrating, nourishing, and protecting the skin barrier.
- Early Detection: Cosmetics can help in early detection of skin cancer by highlighting changes in skin appearance, such as new moles or unusual pigmentation.
Potential Risks:
- Phototoxicity: Certain cosmetic ingredients can increase the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight, leading to increased sun damage and potentially higher cancer risk.
- Chemical Exposure: Some cosmetic ingredients, particularly those found in fragrances, preservatives, and colorants, can be potential irritants or allergens, potentially contributing to skin inflammation and damage.
- Hormonal Disruptors: Certain chemicals found in cosmetics, such as parabens and phthalates, have been linked to hormonal disruption, which could potentially influence skin cell growth and increase cancer risk.
Navigating the Complex Landscape: Key Considerations
Given the potential benefits and risks associated with cosmetics, it is essential to approach skincare practices with informed awareness.
- Sunscreen is Non-Negotiable: Regardless of cosmetic use, consistent and adequate sunscreen application is crucial for protecting the skin from UV radiation and reducing skin cancer risk. Choose broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Ingredient Awareness: Become familiar with the ingredients in your cosmetic products. Opt for products with fewer and simpler ingredients, avoiding potentially harmful chemicals and fragrances. Look for products labeled "non-comedogenic" (less likely to clog pores) and "hypoallergenic" (less likely to cause allergic reactions).
- Patch Testing: Before applying any new cosmetic product, perform a patch test on a small area of skin to check for sensitivity or allergic reactions.
- Professional Consultation: Consult a dermatologist for personalized skincare advice, particularly if you have a family history of skin cancer, have concerns about your skin health, or are unsure about the potential impact of specific cosmetic ingredients.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can cosmetics cause skin cancer?
A: While cosmetics themselves do not directly cause skin cancer, certain ingredients can contribute to skin damage and increase the risk of developing the disease. The primary concern is the potential for phototoxicity, where ingredients can enhance the skin’s sensitivity to UV radiation, leading to increased sun damage.
Q: Are all cosmetics harmful for skin health?
A: Not all cosmetics pose a risk to skin health. Many products are formulated with safe and effective ingredients that can benefit the skin. However, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks associated with certain ingredients and to choose products carefully.
Q: How can I choose safe and effective cosmetics?
A: Look for products with fewer and simpler ingredients, avoiding potential irritants and allergens. Choose products labeled "non-comedogenic" and "hypoallergenic." Consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations based on your skin type and concerns.
Q: What are the best practices for sun protection while using cosmetics?
A: Apply sunscreen liberally and consistently, even when using cosmetics with SPF. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. Choose cosmetics with broad-spectrum SPF protection of 30 or higher.
Q: How can I identify potential signs of skin cancer?
A: Be vigilant about any changes in your skin, including new moles, unusual pigmentation, or sores that don’t heal. Consult a dermatologist for any suspicious skin lesions.
Tips for Safe and Informed Cosmetic Use
- Read Labels Carefully: Pay attention to the ingredients listed on cosmetic products and research potential risks associated with specific chemicals.
- Choose Products with Minimal Ingredients: Opt for products with simpler formulations and fewer ingredients, reducing the likelihood of potential irritants or allergens.
- Avoid Excessive Use: Avoid applying excessive amounts of cosmetics, especially those containing potentially harmful ingredients.
- Use Products as Directed: Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and avoid applying products beyond their intended use.
- Store Cosmetics Properly: Store cosmetics in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat, to maintain their effectiveness and minimize the risk of bacterial growth.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Skin Health
The relationship between skin cancer and cosmetics is multifaceted and requires a balanced approach. While cosmetics can offer potential benefits for skin health, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with certain ingredients and to prioritize safe and informed skincare practices.
By understanding the key factors influencing skin cancer development and the potential impact of cosmetics on skin health, individuals can make informed decisions about their skincare routines, minimizing risks and promoting overall well-being. Regular skin checks, consistent sunscreen use, and a vigilant approach to cosmetic choices are crucial for maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Skin Cancer and Cosmetics: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!