The Science of Skin Products: A Journey into the Dermis
Related Articles: The Science of Skin Products: A Journey into the Dermis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Science of Skin Products: A Journey into the Dermis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Skin Products: A Journey into the Dermis
The human skin, our largest organ, is a remarkable marvel of biology. It serves as a protective barrier against the environment, regulates body temperature, and even plays a role in our immune system. However, this intricate structure is also susceptible to various external and internal stressors, leading to a range of skin concerns. This is where the science of skin products comes into play, offering a myriad of solutions to address these challenges and enhance the overall health and appearance of our skin.
Understanding the Skin’s Structure and Function:
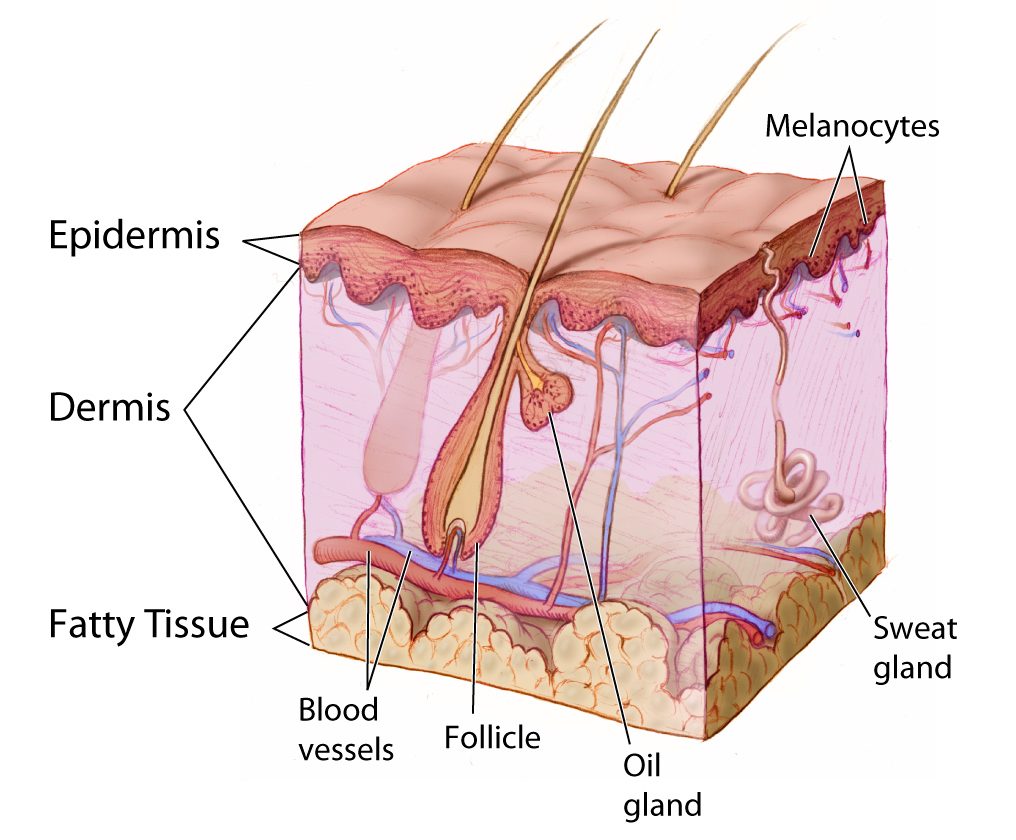
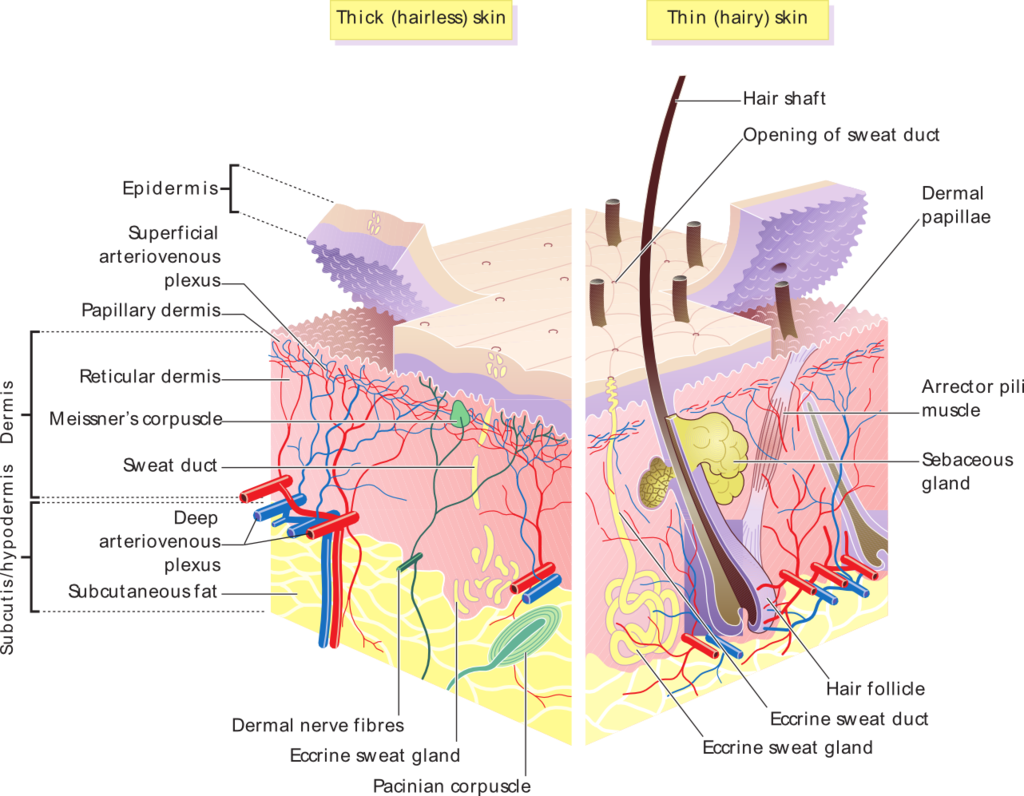
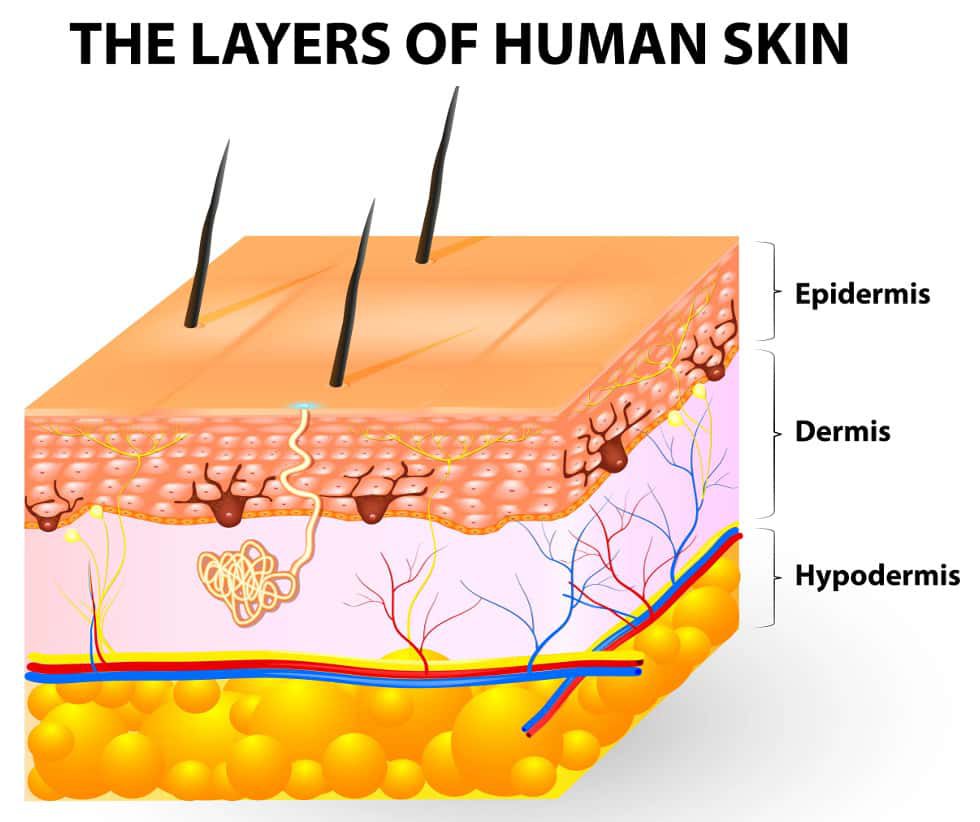
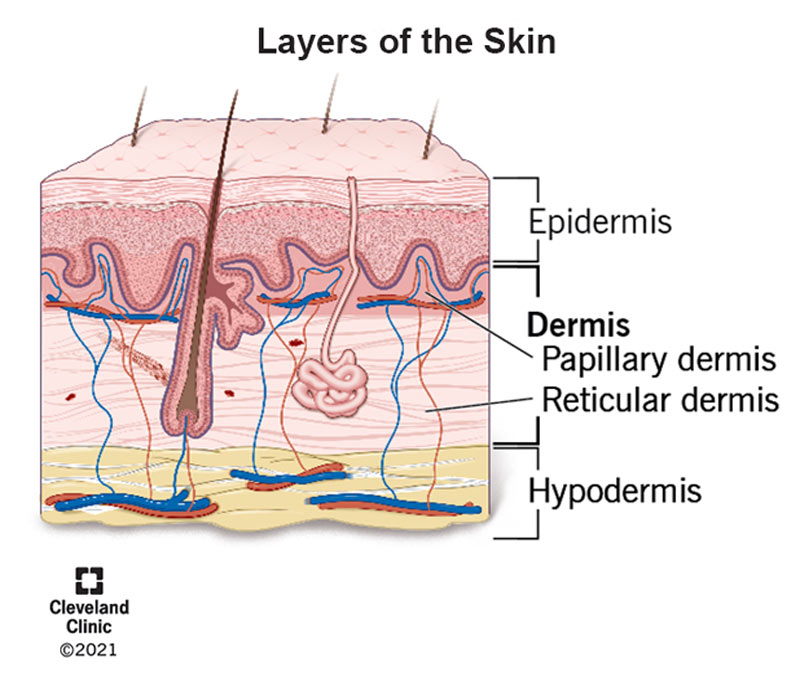
To comprehend the science behind skin products, it is crucial to delve into the skin’s anatomy and physiology. The skin comprises three primary layers:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, responsible for protection and acting as a barrier against water loss and external elements. It is composed of keratinocytes, the cells that produce keratin, a tough protein that forms the outermost layer of the skin.
- Dermis: The middle layer, containing blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It provides structural support and elasticity to the skin.
- Hypodermis: The innermost layer, composed of fat cells and connective tissue, acts as an insulator and energy reserve.
Within the epidermis, there are further sub-layers, each with specific functions. The stratum corneum, the most superficial layer, is responsible for the skin’s barrier function. This layer is constantly being shed and replaced by new cells from the lower layers.
The Science of Skin Product Ingredients:
The effectiveness of skin products lies in their carefully chosen ingredients. These ingredients can be broadly categorized into:
- Moisturizers: These ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides, help retain moisture in the skin, improving its hydration and reducing dryness.
- Sunscreens: These ingredients, like zinc oxide and avobenzone, protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is a major contributor to premature aging and skin cancer.
- Antioxidants: These ingredients, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and green tea extract, combat free radical damage, which can lead to oxidative stress and skin aging.
- Exfoliants: These ingredients, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), remove dead skin cells, revealing smoother, brighter skin.
- Retinoids: These derivatives of vitamin A, like retinol and tretinoin, stimulate collagen production, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and improve skin texture.
- Peptides: These small protein fragments, such as palmitoyl pentapeptide-4, can stimulate collagen synthesis and enhance skin elasticity.
- Anti-Inflammatories: These ingredients, such as niacinamide and licorice root extract, reduce inflammation, redness, and irritation.
The Science of Skin Product Delivery Systems:
Beyond the ingredients themselves, the way they are delivered to the skin plays a crucial role in their effectiveness. This is where the science of delivery systems comes into play.
- Topical Application: Most skin products are applied topically, meaning they are directly applied to the skin’s surface. The effectiveness of topical application depends on the product’s formulation, including its viscosity, pH, and the size of the molecules it contains.
- Transdermal Delivery: This method utilizes specific carriers, such as liposomes or microneedles, to enhance the penetration of active ingredients into deeper layers of the skin.
- Nano-Delivery Systems: This approach utilizes nanoparticles to encapsulate active ingredients, allowing for targeted delivery and improved penetration.
The Science of Skin Product Testing:
To ensure the safety and efficacy of skin products, rigorous testing is essential. This includes:
- In Vitro Testing: This type of testing is conducted on cells or tissues in a laboratory setting, allowing researchers to assess the product’s potential effects on specific skin functions.
- In Vivo Testing: This type of testing is conducted on living organisms, typically animals, to evaluate the product’s safety and efficacy in a more realistic setting.
- Clinical Trials: These trials involve human participants and are designed to assess the effectiveness of a product in treating specific skin conditions or improving overall skin health.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Science of Skin Products:
1. What are the benefits of using skin products?
Skin products offer numerous benefits, including:
- Protection from environmental damage: Sunscreens protect the skin from harmful UV radiation, while antioxidants combat free radical damage.
- Improved skin hydration: Moisturizers and humectants help retain moisture, reducing dryness and improving skin texture.
- Reduction of skin imperfections: Exfoliants remove dead skin cells, while retinoids and peptides stimulate collagen production, reducing fine lines, wrinkles, and acne.
- Enhanced skin tone and texture: Anti-inflammatory ingredients reduce redness and irritation, while brightening agents promote a more even skin tone.
2. Are all skin products safe to use?
Not all skin products are created equal. Some products may contain ingredients that can cause irritation, allergic reactions, or other adverse effects. It is crucial to select products from reputable brands and consult with a dermatologist if you have any concerns.
3. How do I choose the right skin products for my skin type?
The best skin products for you will depend on your individual skin type and concerns. Consider factors like:
- Skin type: Oily, dry, combination, sensitive.
- Skin concerns: Acne, wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, dryness.
- Lifestyle: Exposure to sun, pollution, stress levels.
4. How often should I use skin products?
The frequency of use varies depending on the specific product and your skin type. Consult the product instructions or your dermatologist for guidance.
5. Can I use multiple skin products at the same time?
Using multiple skin products simultaneously can be beneficial, but it is important to ensure that the ingredients are compatible. Consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional for personalized recommendations.
Tips for Using Skin Products Effectively:
- Cleanse your skin thoroughly before applying any products.
- Apply products in the order of consistency, from thinnest to thickest.
- Use sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days.
- Be patient and consistent with your skincare routine.
- Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Conclusion:
The science of skin products is a constantly evolving field, with new ingredients and technologies emerging regularly. By understanding the basic principles of skin structure, function, and product ingredients, consumers can make informed choices about the products they use. Choosing products from reputable brands and consulting with a dermatologist can help ensure that you are using safe and effective products that meet your individual needs. Ultimately, embracing a comprehensive skincare routine based on sound scientific principles can help you achieve healthier, more radiant skin.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Skin Products: A Journey into the Dermis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
