The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen Serums
Related Articles: The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen Serums
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen Serums. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen Serums
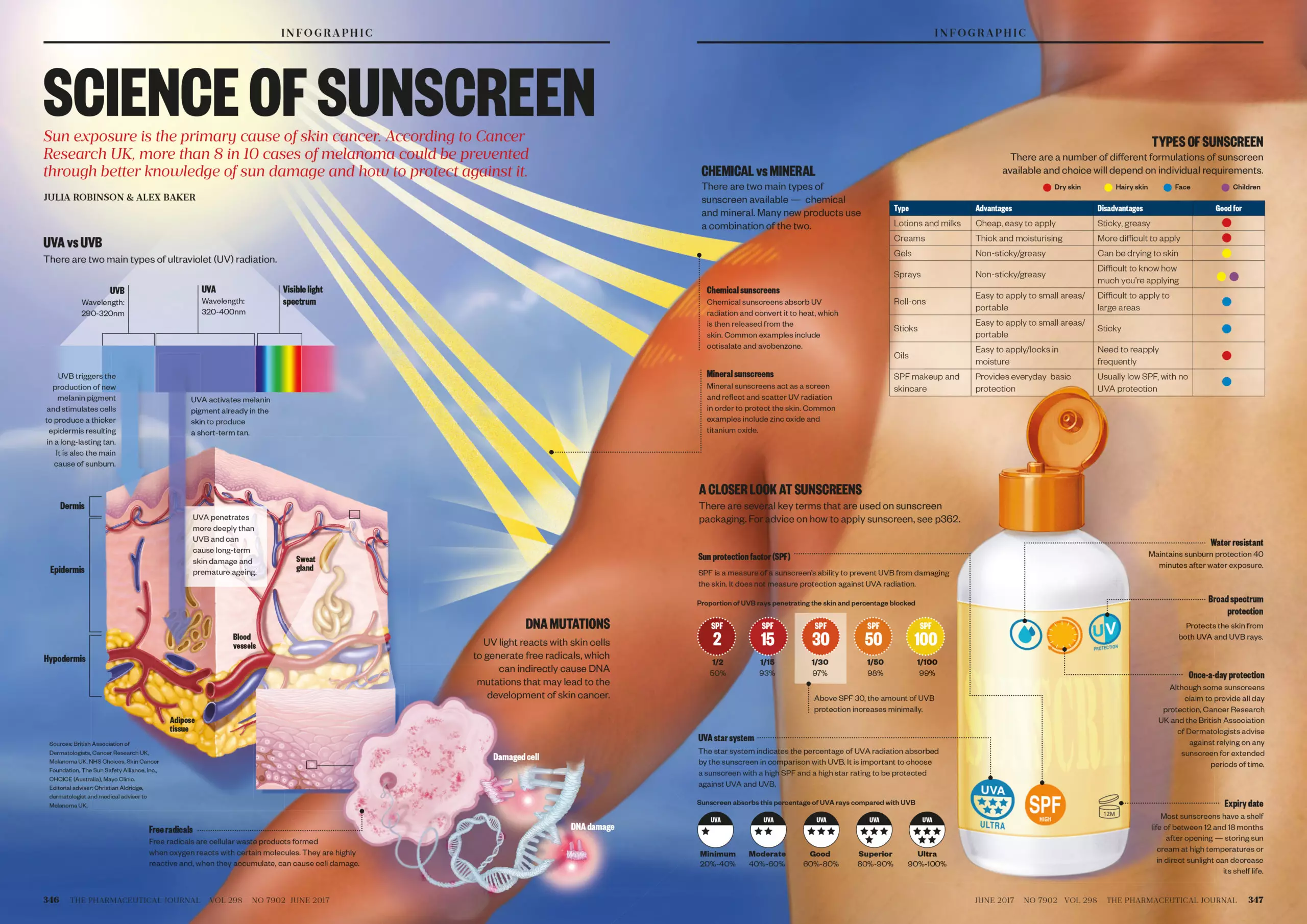
The sun, while essential for life, also poses a significant threat to human health. Its ultraviolet (UV) radiation, particularly the harmful UVA and UVB rays, can cause a range of issues, from premature skin aging to skin cancer. This is where sun protection becomes paramount, and in recent years, sunscreen serums have emerged as a popular and effective solution.
This article delves into the world of sunscreen serums, exploring their composition, benefits, and proper usage. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of these potent skincare products and their role in safeguarding the skin from the sun’s damaging effects.
Understanding the Sun’s Impact on Skin
The sun emits various types of radiation, with UVA and UVB rays being the most concerning for skin health.
-
UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin, causing damage to collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. They also contribute to skin cancer development.
-
UVB rays are responsible for sunburn, causing immediate damage to the skin’s surface. Prolonged exposure can lead to skin cancer and premature aging.
Sunscreen Serums: A Modern Approach to Sun Protection
Sunscreen serums are lightweight, fast-absorbing formulas that provide broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays. They are formulated with a high concentration of sunscreen filters, often combined with other beneficial ingredients for skincare.
Key Ingredients in Sunscreen Serums
-
Sunscreen Filters: These are the primary active ingredients in sunscreen serums, absorbing or reflecting UV rays to prevent them from reaching the skin. Common filters include:
- Chemical Filters: These absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat, which is then dissipated. Examples include oxybenzone, octinoxate, avobenzone, and octisalate.
- Mineral Filters: These physically block UV rays, reflecting them away from the skin. Examples include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
-
Antioxidants: These ingredients help combat free radical damage caused by UV exposure, protecting the skin from oxidative stress. Examples include vitamin C, vitamin E, and green tea extract.
-
Moisturizers: Sunscreen serums often contain humectants like hyaluronic acid to hydrate the skin, preventing dryness and enhancing the overall texture.
-
Other Beneficial Ingredients: Some serums may include ingredients like niacinamide, peptides, or ceramides to address specific skin concerns, such as hyperpigmentation, wrinkles, or dryness.
Benefits of Using Sunscreen Serums
-
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Sunscreen serums offer comprehensive protection against both UVA and UVB rays, safeguarding the skin from a wide range of sun-related damage.
-
Lightweight and Fast-Absorbing: Their lightweight texture and fast-absorbing properties make them ideal for daily use, ensuring a comfortable application without leaving a greasy or white cast.
-
Skincare Benefits: Many sunscreen serums incorporate additional skincare ingredients, providing benefits beyond sun protection, such as hydration, anti-aging, and brightening.
-
Convenient Application: The serum format allows for easy and precise application, ensuring even coverage on all areas of the face and body.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen Serum
Selecting the appropriate sunscreen serum involves considering several factors:
-
Sun Protection Factor (SPF): Choose a serum with an SPF of at least 30, which blocks 97% of UVB rays. Higher SPFs offer greater protection, but they may not necessarily be more effective for daily use.
-
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Ensure the serum protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Look for the words "broad-spectrum" on the product label.
-
Skin Type: Consider your skin type and choose a serum formulated for your specific needs. For example, oily skin may benefit from a lightweight, oil-free serum, while dry skin may prefer a moisturizing formula.
-
Ingredients: Check the ingredient list for potential allergens or irritants. If you have sensitive skin, opt for a fragrance-free and hypoallergenic serum.
How to Apply Sunscreen Serum
-
Clean Skin: Apply sunscreen serum to clean, dry skin.
-
Amount: Use a generous amount, about a teaspoonful for the face and neck.
-
Even Coverage: Apply the serum evenly, paying attention to areas often missed, such as the ears, eyelids, and back of the neck.
-
Reapplication: Reapply every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
FAQs on Sunscreen Serums
1. Can Sunscreen Serums Be Used Under Makeup?
Yes, many sunscreen serums are formulated to be lightweight and compatible with makeup. They can be applied as a primer before makeup, creating a smooth base for foundation and other products.
2. Are Sunscreen Serums Water-Resistant?
Some sunscreen serums offer water resistance, but it is essential to check the product label for specific details. Water resistance is indicated by a time limit, such as "water-resistant for 80 minutes."
3. Can Sunscreen Serums Cause Breakouts?
While most sunscreen serums are non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores), some individuals may experience breakouts. It’s advisable to test the serum on a small area of skin before applying it to the entire face.
4. How Long Does Sunscreen Serum Last?
The shelf life of sunscreen serum typically ranges from 2 to 3 years, depending on the specific ingredients and storage conditions. Check the product label for the expiration date.
5. Can Sunscreen Serums Be Used on All Skin Types?
Sunscreen serums are generally suitable for all skin types, but it’s crucial to choose a formula tailored to your specific needs. For sensitive skin, opt for a hypoallergenic and fragrance-free serum.
Tips for Using Sunscreen Serums
-
Apply Sunscreen Serum Daily: Make sun protection a daily habit, even on cloudy days. UV rays can penetrate clouds and still damage the skin.
-
Protect Your Lips: Use a lip balm with SPF to protect your lips from sun damage.
-
Wear Protective Clothing: Cover up with clothing that offers UV protection, such as long sleeves, pants, and hats.
-
Seek Shade: Avoid direct sunlight during peak hours, typically between 10 am and 4 pm.
-
Check the Expiration Date: Replace your sunscreen serum every year or when the expiration date is reached.
Conclusion
Sunscreen serums play a vital role in protecting the skin from the sun’s harmful rays. By providing broad-spectrum protection, incorporating skincare benefits, and offering a convenient application, they have become an essential component of a comprehensive skincare routine. Choosing the right sunscreen serum and using it correctly can significantly reduce the risk of sun-related damage, promoting healthy and radiant skin for years to come.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen Serums. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!