The Vital Connection: Skin and Vitamin D
Related Articles: The Vital Connection: Skin and Vitamin D
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Vital Connection: Skin and Vitamin D. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Vital Connection: Skin and Vitamin D

The human body is a complex and interconnected system, with each organ playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Among these vital components, the skin and vitamin D share a unique and intricate relationship, one that is essential for optimal functioning. This article delves into the fascinating world of skin and vitamin D, exploring their individual roles, their symbiotic connection, and the implications for human health.
The Skin: Our Protective Barrier
The skin, the largest organ in the human body, serves as our primary defense against the external environment. This intricate, multi-layered structure acts as a shield, protecting us from physical injury, microbial invasion, and harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The skin is also responsible for regulating body temperature, maintaining hydration, and contributing to our sense of touch.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
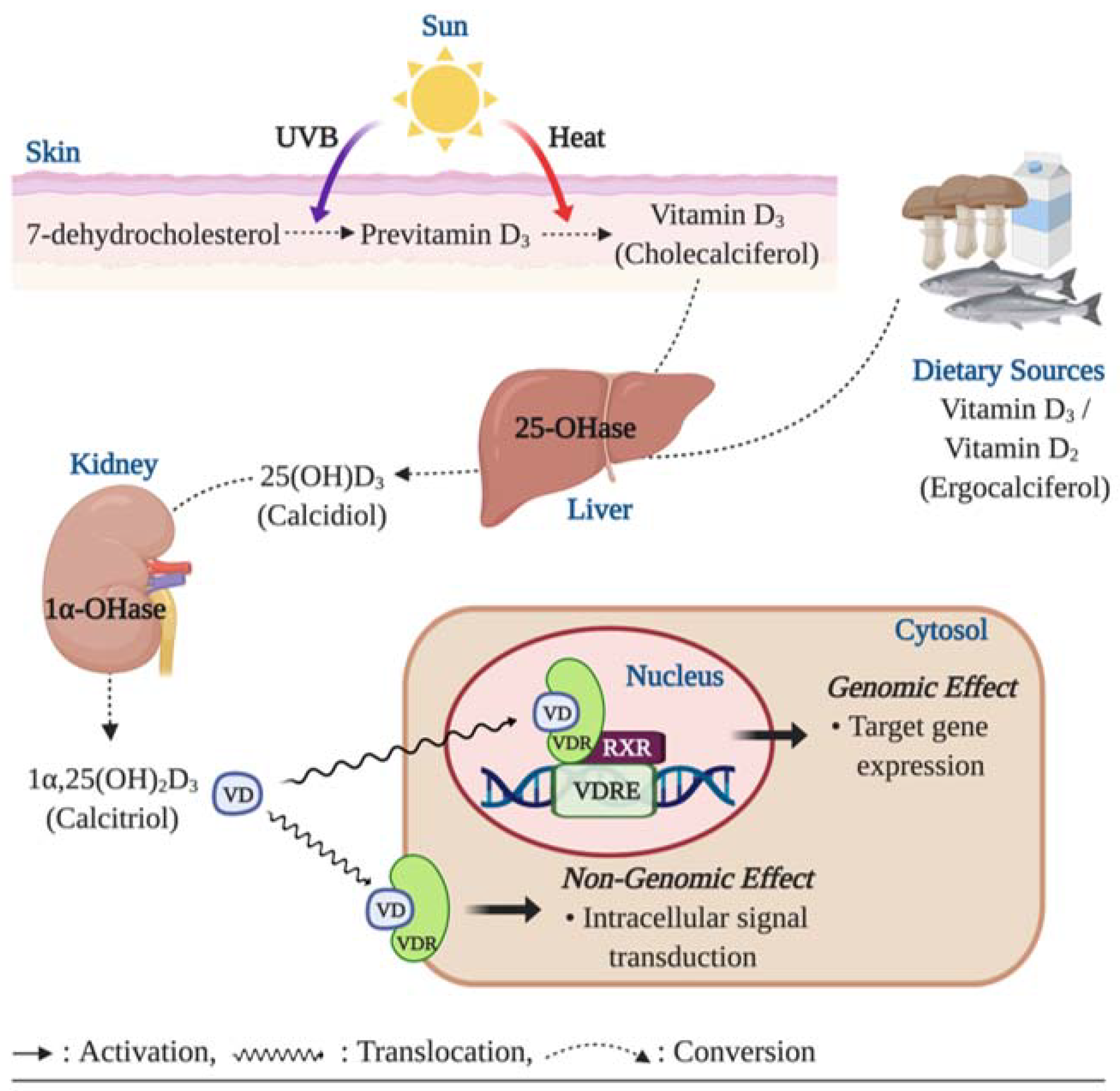
Vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," is a fat-soluble nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining calcium homeostasis, bone health, and immune function. While it can be obtained through dietary sources like fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods, the majority of our vitamin D is synthesized in the skin through a complex process triggered by exposure to sunlight.
The Skin’s Role in Vitamin D Synthesis
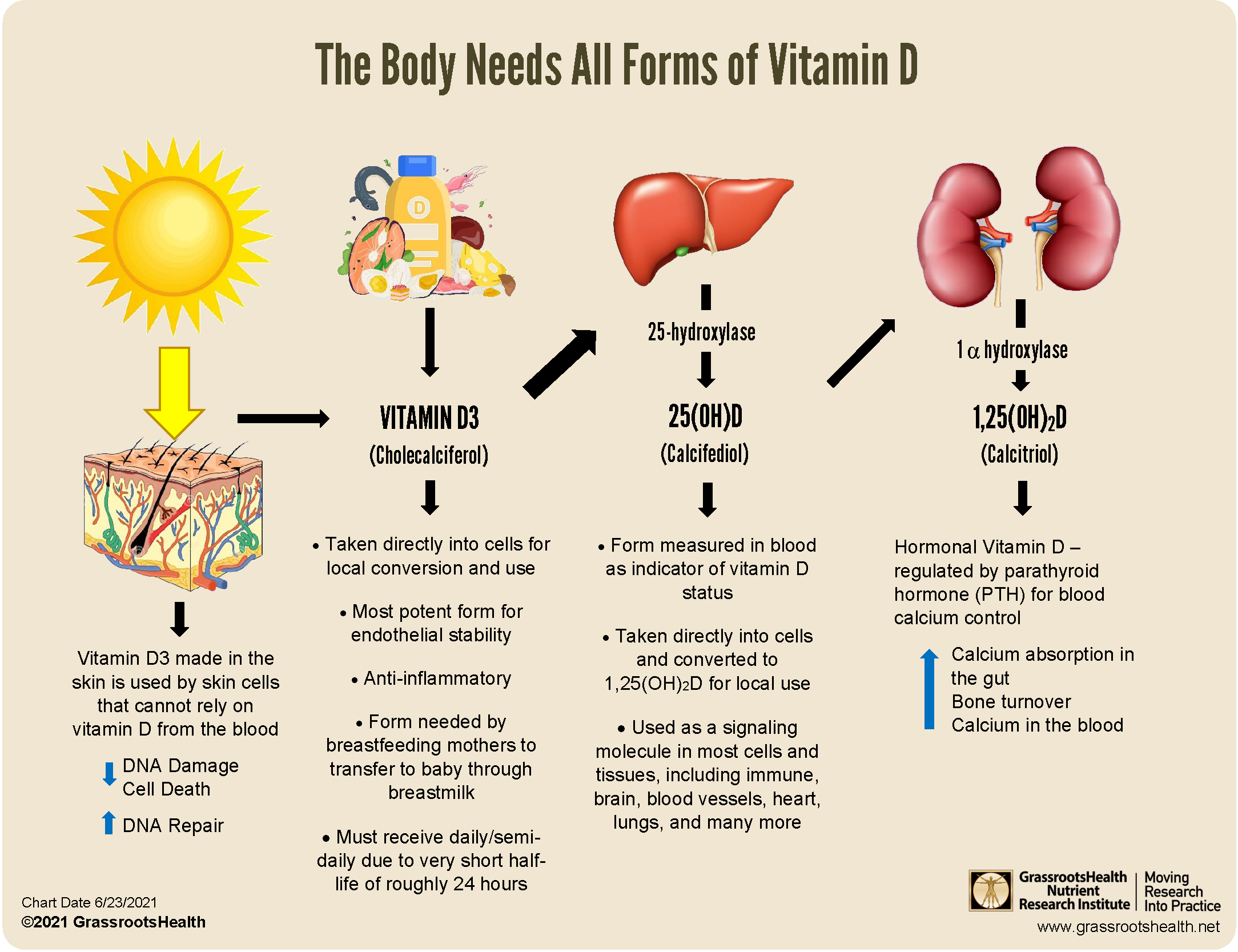
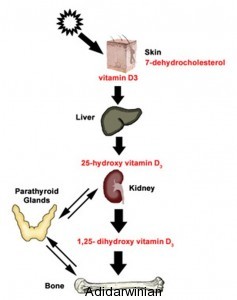
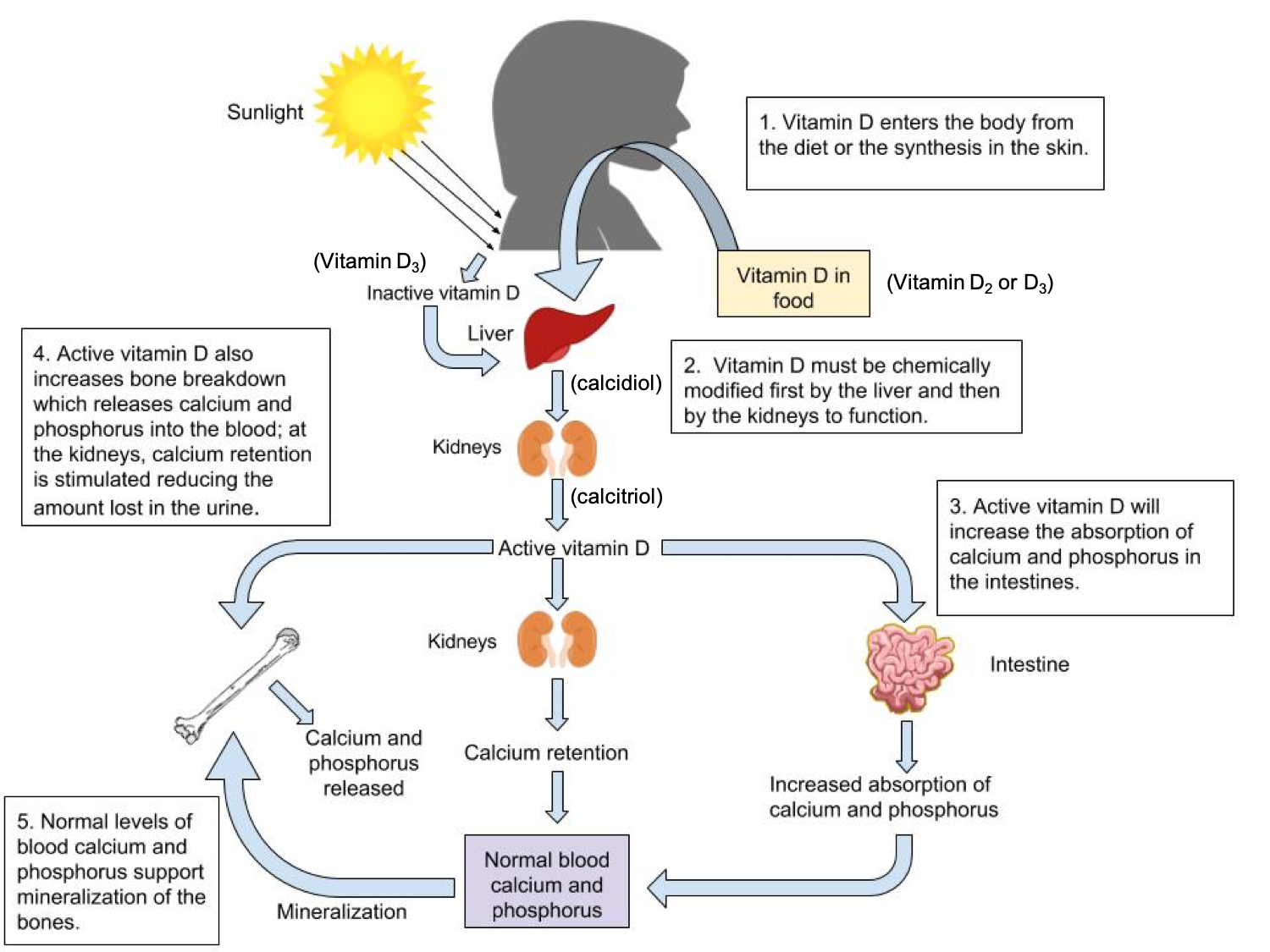
When ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from sunlight strike the skin, they interact with a cholesterol-like molecule called 7-dehydrocholesterol, initiating a series of biochemical reactions. This process ultimately leads to the formation of pre-vitamin D3, which is then converted into the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, in the liver and kidneys. This intricate process demonstrates the crucial role the skin plays in providing the body with this essential nutrient.
Benefits of Adequate Vitamin D
The benefits of adequate vitamin D levels extend far beyond bone health. Research has established a strong link between vitamin D deficiency and various health conditions, including:
- Bone Health: Vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption, which is essential for strong bones and the prevention of osteoporosis.
- Immune Function: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses, helping to protect against infections and autoimmune diseases.
- Cardiovascular Health: Studies suggest that vitamin D may help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Cancer Prevention: Some research indicates that vitamin D may have a protective effect against certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, and prostate cancer.
- Mental Health: Emerging evidence suggests a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and depression, although further research is needed.
The Impact of Sun Exposure on Skin Health
While sunlight is essential for vitamin D synthesis, excessive exposure can have detrimental effects on the skin. UVB radiation, responsible for vitamin D production, can also damage DNA and contribute to premature aging, skin cancer, and other skin problems.
Balancing the Need for Sunlight and Skin Protection
Maintaining optimal vitamin D levels while protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation requires a delicate balance. The following strategies can help achieve this balance:
- Limited Sun Exposure: Aim for short periods of sun exposure, especially during the midday hours when UVB radiation is strongest.
- Sunscreen Application: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect the skin from both UVA and UVB rays.
- Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing like long sleeves, pants, and hats, especially during prolonged sun exposure.
- Supplementation: Consider vitamin D supplementation, especially during winter months or if you have limited sun exposure.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Synthesis
The amount of vitamin D synthesized in the skin is influenced by several factors, including:
- Skin Pigmentation: Darker skin pigmentation requires more sun exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as lighter skin.
- Age: As we age, the skin’s ability to synthesize vitamin D decreases.
- Geographic Location: Individuals living in regions with less sunlight exposure are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency.
- Time of Day: UVB radiation is strongest between 10:00 AM and 4:00 PM.
- Season: Vitamin D synthesis is reduced during winter months due to shorter days and lower sun angles.
- Cloud Cover: Cloud cover significantly reduces the amount of UVB radiation reaching the skin.
- Clothing: Covering the skin with clothing reduces vitamin D synthesis.
Vitamin D Deficiency: A Growing Concern
Vitamin D deficiency, known as hypovitaminosis D, is a widespread public health concern. Several factors contribute to this issue, including:
- Limited Sun Exposure: Modern lifestyles often involve spending less time outdoors, leading to reduced sun exposure.
- Increased Indoor Time: Working indoors, using public transportation, and engaging in indoor activities further limit sun exposure.
- Sunscreen Use: While essential for skin protection, sunscreen can reduce vitamin D synthesis.
- Dietary Deficiencies: Some individuals may not consume sufficient amounts of vitamin D-rich foods.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as malabsorption disorders and kidney disease, can impair vitamin D absorption and metabolism.
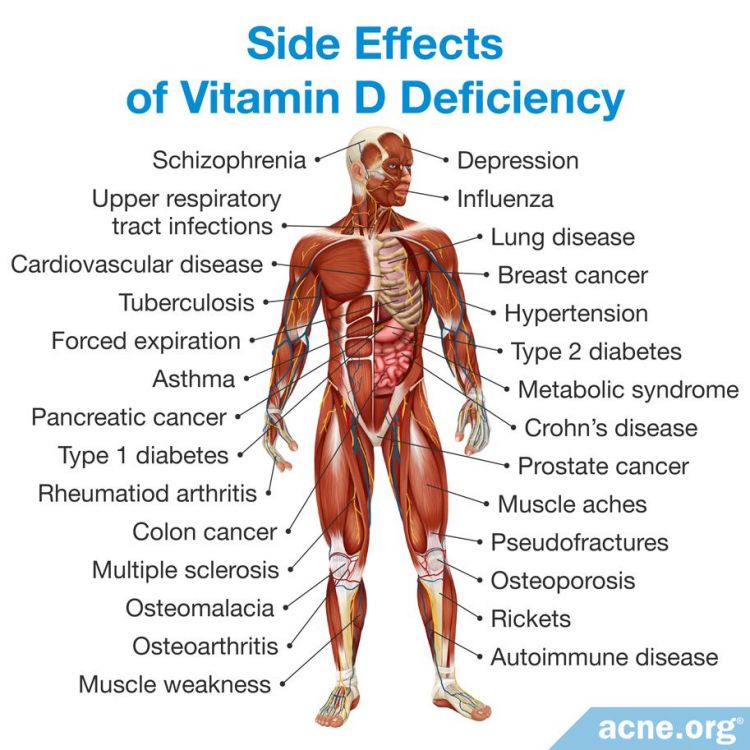
Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- Rickets: A condition that affects children, characterized by bone softening and skeletal deformities.
- Osteoporosis: A condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
- Muscle Weakness: Vitamin D deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune function, and deficiency can increase susceptibility to infections.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Some studies suggest a link between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune diseases.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Vitamin D deficiency may contribute to cardiovascular disease.
- Cancer: Some research indicates that vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of certain cancers.
Assessing Vitamin D Levels
If you are concerned about your vitamin D levels, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can recommend a blood test to assess your vitamin D status and advise on appropriate treatment or preventive measures.
Treatment for Vitamin D Deficiency
Treatment for vitamin D deficiency typically involves vitamin D supplementation. The recommended dosage varies depending on the severity of the deficiency and individual factors.
Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency
Preventing vitamin D deficiency involves optimizing sun exposure, consuming vitamin D-rich foods, and considering supplementation if necessary.
FAQs about Skin and Vitamin D
Q: How much sun exposure is needed for adequate vitamin D synthesis?
A: The amount of sun exposure required for adequate vitamin D synthesis varies depending on factors like skin pigmentation, age, geographic location, and time of year. However, a general guideline is to aim for 10-15 minutes of sun exposure to the face, arms, and legs without sunscreen 2-3 times per week.
Q: Can I get enough vitamin D from food alone?
A: While certain foods are rich in vitamin D, it is difficult to obtain sufficient amounts solely through diet.
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency?
A: Signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency can be subtle and vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. Common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, and mood changes.
Q: What are the risks of taking too much vitamin D?
A: Excessive vitamin D intake can lead to hypervitaminosis D, which can cause calcium buildup in the blood, leading to kidney stones, nausea, vomiting, and other health problems. It is essential to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before taking vitamin D supplements.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal Vitamin D Levels and Skin Health
- Optimize Sun Exposure: Aim for short periods of sun exposure, especially during the midday hours when UVB radiation is strongest.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Cover exposed skin with protective clothing like long sleeves, pants, and hats during prolonged sun exposure.
- Consume Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Include fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods in your diet.
- Consider Supplementation: Consult with a healthcare professional about vitamin D supplementation, especially during winter months or if you have limited sun exposure.
- Regular Skin Checks: Conduct regular skin checks for any changes in moles, skin lesions, or other abnormalities. Consult a dermatologist if you notice any concerning changes.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between skin and vitamin D is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding the role of the skin in vitamin D synthesis, the benefits of adequate vitamin D levels, and the potential consequences of deficiency is crucial for making informed decisions about sun exposure, diet, and supplementation. By balancing the need for sunlight with the importance of skin protection, individuals can optimize their vitamin D levels while safeguarding their skin health. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on maintaining optimal vitamin D levels and ensuring healthy skin.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Vital Connection: Skin and Vitamin D. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!