Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health
Related Articles: Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health
- 3.1 Common Skin Concerns and Their Causes
- 3.2 Treatment Options for Skin Concerns
- 3.3 FAQs About Skin Concerns
- 3.4 Tips for Maintaining Skin Health
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health
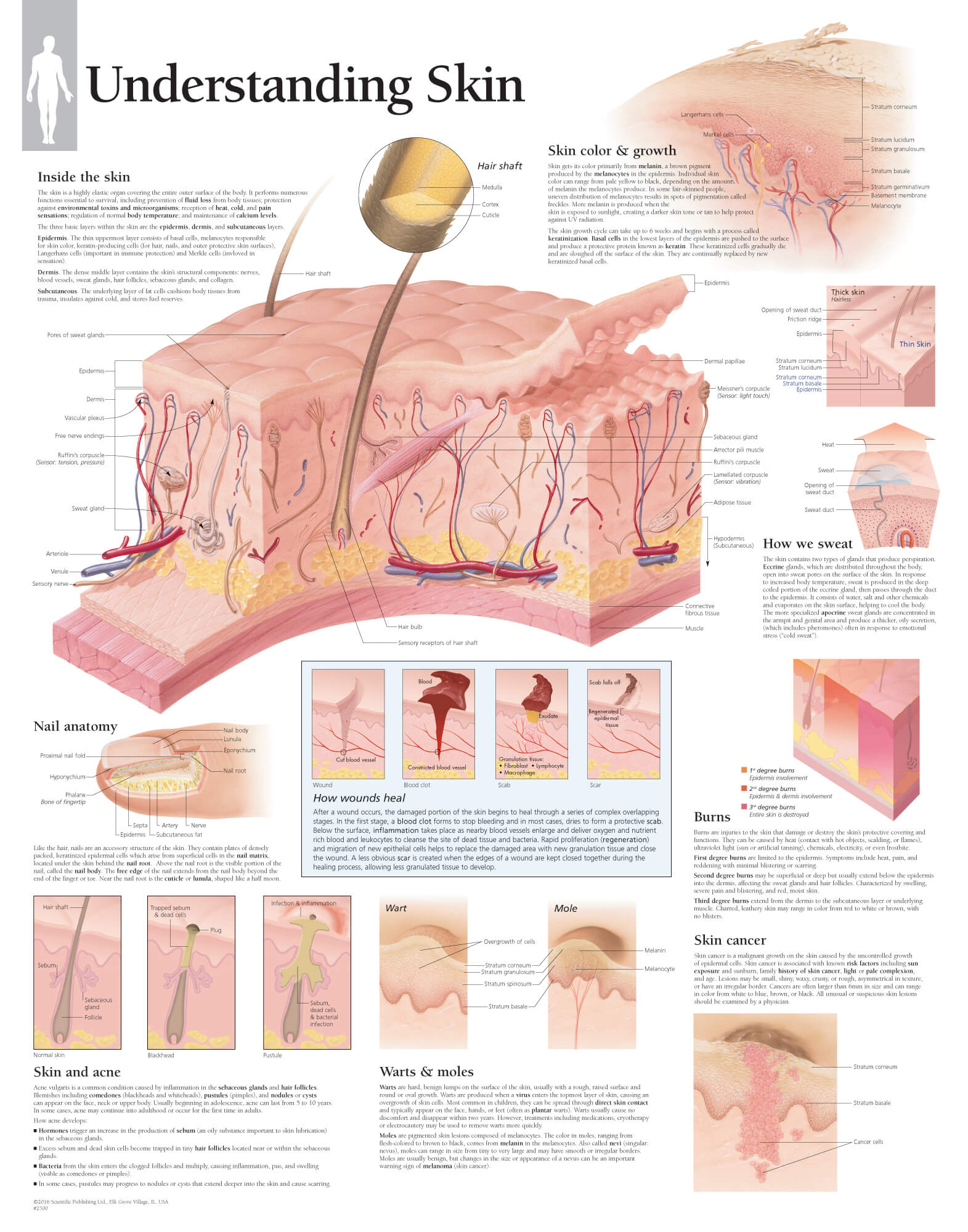
The human skin, the largest organ in the body, acts as a barrier against the environment and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. However, various factors can disrupt its delicate balance, leading to a wide range of skin concerns. These concerns can manifest as dryness, oiliness, acne, wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, and other issues, impacting both physical appearance and emotional well-being.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of common skin concerns, exploring the underlying causes, available treatment options, and preventive measures. By gaining a deeper insight into the complexities of skin health, individuals can make informed decisions about their skincare routine and seek professional guidance when necessary.
Common Skin Concerns and Their Causes
1. Dryness:
Dry skin occurs when the skin lacks sufficient moisture, often due to:
- Environmental factors: Cold, dry weather, low humidity, and excessive sun exposure can strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Age: As we age, the skin’s ability to retain moisture diminishes, leading to increased dryness.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, and hypothyroidism, can contribute to dry skin.
- Medications: Some medications, including diuretics and retinoids, can have a drying effect on the skin.
- Harsh skincare products: Using products with harsh chemicals or alcohol can disrupt the skin’s natural moisture barrier.
2. Oiliness:
Oily skin is characterized by excessive sebum production, resulting in a shiny, greasy appearance. Contributing factors include:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy can trigger increased sebum production.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to oily skin.
- Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fatty foods and processed sugars can exacerbate oiliness.
- Stress: Stress can stimulate the sebaceous glands, leading to increased oil production.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase sebum production.
3. Acne:
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by pimples, whiteheads, blackheads, and cysts. It is primarily caused by:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Androgens, hormones present in both men and women, can stimulate sebum production, leading to acne.
- Excess sebum: Overproduction of sebum can clog pores, creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a type of bacteria commonly found on the skin, can trigger inflammation and acne breakouts.
- Dead skin cells: Accumulation of dead skin cells can clog pores, contributing to acne formation.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to acne.
4. Wrinkles:
Wrinkles are lines on the skin that appear as a result of aging and sun damage. They are caused by:
- Loss of collagen and elastin: As we age, the skin’s production of collagen and elastin, proteins responsible for skin elasticity, declines, leading to wrinkles.
- Sun damage: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun breaks down collagen and elastin, accelerating the aging process and contributing to wrinkle formation.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, hindering collagen production and contributing to wrinkles.
- Facial expressions: Repeated facial expressions, such as frowning and smiling, can lead to the formation of wrinkles over time.
5. Hyperpigmentation:
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of skin patches due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Common causes include:
- Sun exposure: Excessive sun exposure can stimulate melanin production, leading to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can trigger hyperpigmentation.
- Inflammation: Skin inflammation, such as that caused by acne or eczema, can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antibiotics and birth control pills, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
6. Rosacea:
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by redness, flushing, and bumps on the face. It is believed to be caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of rosacea are more likely to develop the condition.
- Environmental triggers: Sun exposure, heat, cold, wind, and spicy foods can trigger rosacea flare-ups.
- Inflammatory response: Rosacea is thought to involve an overactive inflammatory response in the skin.
- Microscopic mites: Demodex mites, tiny creatures that live on the skin, may play a role in rosacea.
Treatment Options for Skin Concerns
The treatment approach for skin concerns depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Topical Medications:
- Moisturizers: Dry skin can be treated with moisturizers to replenish moisture and improve skin hydration.
- Retinoids: Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that can reduce acne, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation.
- Benzoyl peroxide: This topical medication kills bacteria and helps unclog pores, effectively treating acne.
- Salicylic acid: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid that exfoliates dead skin cells and helps unclog pores, improving acne and hyperpigmentation.
- Hydrocortisone cream: This steroid cream can reduce inflammation and redness associated with conditions like eczema and rosacea.
2. Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics can be used to treat acne by killing bacteria and reducing inflammation.
- Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin is a powerful oral medication that can effectively treat severe acne.
- Hormonal therapy: Hormonal therapy can be used to manage acne caused by hormonal fluctuations.
3. Light Therapies:
- Photodynamic therapy: This therapy uses light and a photosensitizing agent to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Intense pulsed light (IPL): IPL can be used to treat acne, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation by targeting specific skin structures.
4. Procedures:
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels use acids to remove the top layer of skin, improving acne, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure uses a handheld device to remove the top layer of skin, improving skin texture and reducing wrinkles.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy can be used to treat acne, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation by targeting specific skin structures.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote skin health.
- Adequate hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the skin hydrated and healthy.
- Sun protection: Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily can protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
- Stress management: Stress can worsen skin conditions, so finding healthy ways to manage stress is important.
- Proper skincare routine: Establishing a consistent skincare routine with appropriate products for your skin type can help maintain skin health.
FAQs About Skin Concerns
1. What are the most common skin concerns?
The most common skin concerns include dryness, oiliness, acne, wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, and rosacea. These concerns can vary in severity and impact individuals differently.
2. How can I prevent skin concerns?
Preventing skin concerns involves a multi-pronged approach that includes:
- Sun protection: Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily can prevent sun damage and premature aging.
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote skin health.
- Adequate hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the skin hydrated and healthy.
- Stress management: Finding healthy ways to manage stress can reduce its impact on the skin.
- Proper skincare routine: Establishing a consistent skincare routine with appropriate products for your skin type can help maintain skin health.
3. When should I see a dermatologist?
It is recommended to see a dermatologist if:
- Skin concerns are severe or persistent.
- Home remedies and over-the-counter products are not effective.
- You are experiencing unusual skin changes or symptoms.
- You have a family history of skin conditions.
4. Are there any natural remedies for skin concerns?
Some natural remedies may provide relief for certain skin concerns, but it is important to consult a dermatologist before trying any new remedies. Some commonly used natural remedies include:
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera can soothe irritation and inflammation.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has antibacterial properties and can be used to treat acne.
- Honey: Honey has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Oatmeal: Oatmeal can soothe dry and itchy skin.
5. What are the long-term effects of untreated skin concerns?
Untreated skin concerns can lead to:
- Increased severity of the condition.
- Scarring and permanent skin damage.
- Emotional distress and low self-esteem.
- Increased risk of skin cancer.
Tips for Maintaining Skin Health
- Cleanse your face twice daily: Use a gentle cleanser appropriate for your skin type to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
- Exfoliate regularly: Exfoliating removes dead skin cells and helps unclog pores, improving skin texture and appearance.
- Moisturize daily: Apply a moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and healthy.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Eat a healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote skin health.
- Manage stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress, as it can negatively impact the skin.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for skin repair and rejuvenation.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and alcohol consumption can damage the skin.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy skin requires a holistic approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, proper skincare, and professional consultation when necessary. By understanding the underlying causes of common skin concerns and adopting preventive measures, individuals can minimize the risk of developing these issues and achieve a radiant, healthy complexion. Remember, consulting a dermatologist is crucial for personalized advice and treatment plans.





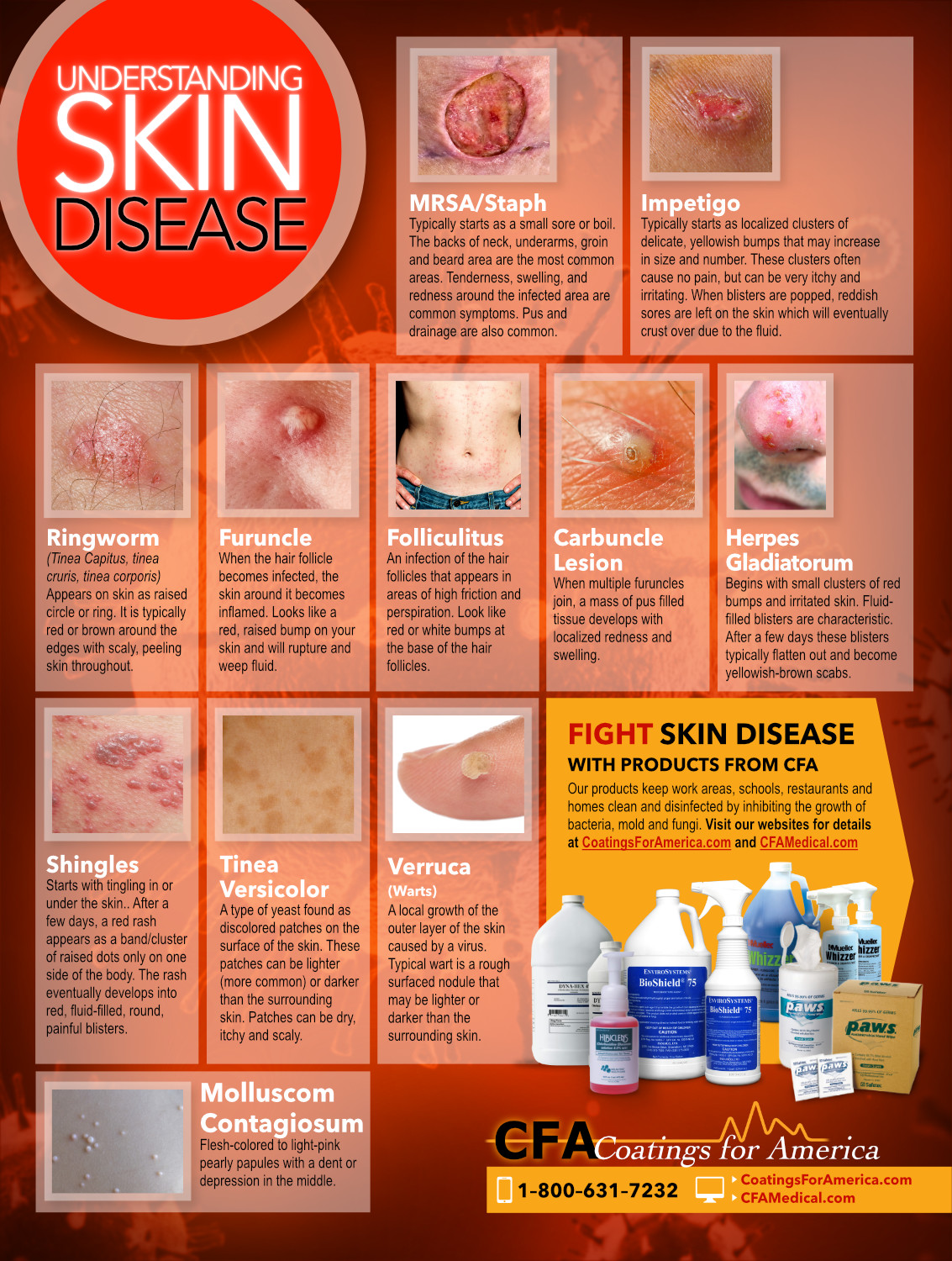


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Skin Concerns: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Health. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!