Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer
Related Articles: Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer

Skin cancer, a prevalent form of cancer, arises from uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within the skin. While various factors contribute to its development, certain elements significantly increase an individual’s susceptibility. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted nature of skin cancer risks, providing a detailed understanding of their impact and potential implications.
Sunlight Exposure: The Primary Culprit
The most significant risk factor for skin cancer is prolonged and excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV rays penetrate the skin, damaging DNA and triggering mutations that can lead to cancerous cell growth. The severity of this damage is influenced by several factors, including:
- Intensity of UV radiation: The intensity of UV radiation varies depending on geographical location, time of day, and season. Regions closer to the equator receive higher UV radiation, while midday hours and summer months generally exhibit increased intensity.
- Duration of exposure: The longer the skin is exposed to UV radiation, the greater the risk of damage.
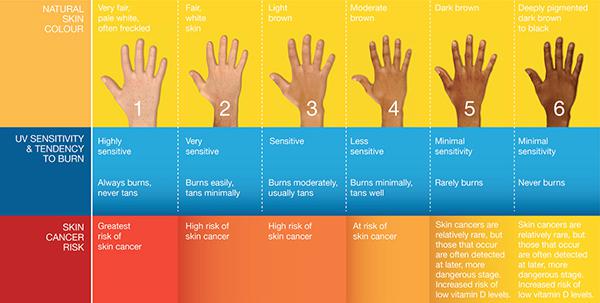
- Skin type: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes are more susceptible to UV damage due to lower melanin production, which offers natural protection from UV radiation.
- Sunburns: Sunburns are a clear indicator of UV damage and significantly increase the risk of skin cancer. Each sunburn, especially in childhood, increases the likelihood of developing skin cancer later in life.
Beyond the Sun: Other Risk Factors
While sunlight exposure is the primary driver of skin cancer, several other factors contribute to its development:
- Family history: Individuals with a family history of skin cancer are at an increased risk. Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in determining susceptibility.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as cumulative UV damage accumulates over time.
- Skin conditions: Certain pre-cancerous skin conditions, such as actinic keratosis, increase the risk of developing invasive skin cancer.
- Immune system deficiencies: Weakened immune systems, often associated with conditions like HIV or organ transplantation, can hinder the body’s ability to fight off cancerous cells.
- Certain medications: Some medications, particularly immunosuppressants, can suppress the immune system, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
- Artificial tanning: Tanning beds and sunlamps emit UV radiation, posing similar risks to sun exposure.
- Chemical exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic, can also increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor diet can contribute to overall health deterioration, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Understanding the Types: A Closer Look
Skin cancer encompasses various types, each with distinct characteristics and risk factors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for early detection and effective treatment:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): The most common type, BCC typically appears as a pearly or waxy bump. It rarely spreads to other parts of the body but can be locally invasive.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): Less common than BCC, SCC appears as a firm, red nodule. It has a higher potential for spreading to other parts of the body.
- Melanoma: The most serious form of skin cancer, melanoma arises from melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation. It can spread rapidly to other organs and is often fatal if not detected and treated early.
Early Detection: The Key to Prevention
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment of skin cancer. Regular skin self-examinations and visits to a dermatologist can identify suspicious lesions, enabling prompt intervention and increasing the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Can I reduce my risk of skin cancer?
A: Yes, several measures can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer:
- Limit sun exposure: Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Wear protective clothing: Cover exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats.
- Use sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every two hours, even on cloudy days.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps: These devices emit UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Q: What are the symptoms of skin cancer?
A: Skin cancer can present with various symptoms, but some common signs include:
- A mole that changes in size, shape, color, or texture.
- A new growth or sore that does not heal.
- A sore that bleeds, crusts, or scabs repeatedly.
- A mole with an irregular border.
- A mole with multiple colors.
- A mole that is larger than 6 millimeters in diameter.
- A raised, pearly or waxy bump.
- A firm, red nodule.
- A scaly, flat lesion.
Q: What should I do if I notice a suspicious lesion?
A: If you notice any of the above symptoms, consult a dermatologist immediately. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Tips for Skin Cancer Prevention
- Practice sun safety: Wear protective clothing, use sunscreen, and avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Perform regular skin self-examinations: Familiarize yourself with your skin and check for any changes in moles or new growths.
- See a dermatologist regularly: Schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist, particularly if you have a family history of skin cancer or have other risk factors.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps: These devices emit UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious health concern, but understanding the risks and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce its incidence. By limiting sun exposure, practicing sun safety, and engaging in regular skin self-examinations, individuals can empower themselves to protect their skin and reduce their risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for favorable outcomes, emphasizing the importance of regular dermatological checkups and awareness of potential symptoms. Through education, prevention, and early intervention, we can strive towards a future where skin cancer becomes a less prevalent threat to human health.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!