Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: 3D Models and the Power of Labeling
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: 3D Models and the Power of Labeling
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: 3D Models and the Power of Labeling. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: 3D Models and the Power of Labeling

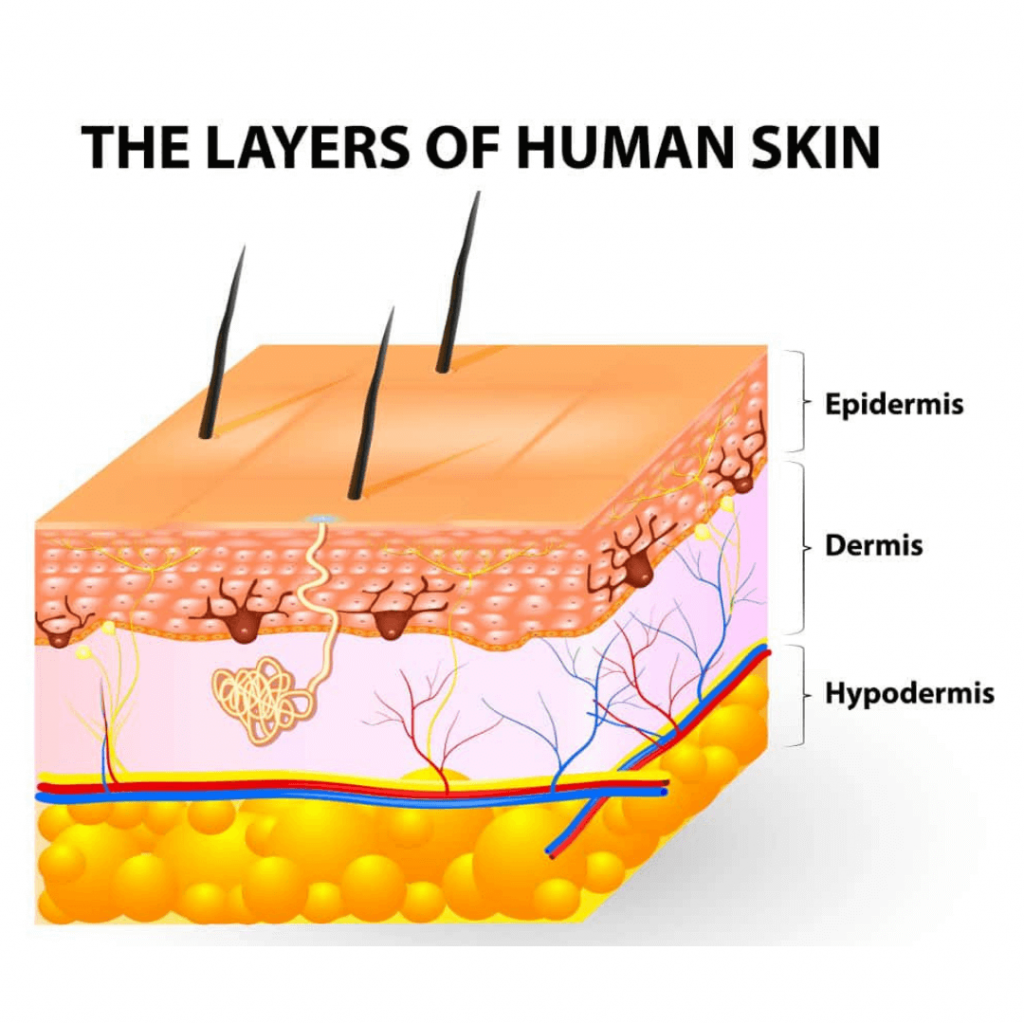
The human skin, our largest organ, is a complex and intricate tapestry of cells, tissues, and structures. Its role extends far beyond simply protecting our internal organs; it plays a crucial part in regulating temperature, sensing the environment, and even contributing to our immune system. Understanding this intricate system is essential for advancing research in dermatology, cosmetics, and medical device development.
This is where 3D models of skin, meticulously labeled with detailed anatomical information, come into play. These models, often created using advanced imaging techniques and computer modeling, offer a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and understanding the complexities of skin structure and function.
The Importance of Labeling in 3D Skin Models
Labeling in 3D skin models is not simply a visual aid; it is a crucial component that unlocks the true potential of these models for research and development. Imagine a detailed map of a city, with each street, landmark, and building clearly labeled. This is analogous to a labeled 3D skin model, providing a comprehensive and accessible roadmap of the skin’s intricate anatomy.
Key Benefits of Labeled 3D Skin Models:
-
Enhanced Visualization and Comprehension: Labeled 3D models allow researchers to visualize and understand the complex interplay of different skin layers, cells, and structures in an interactive and intuitive way.
-
Improved Communication and Collaboration: Clear labeling facilitates communication and collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and other stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding anatomical structures and their functions.
-
Precise Measurement and Analysis: Labeled models enable accurate measurement and analysis of various skin parameters, such as thickness, cell density, and vascularization, facilitating quantitative research and objective comparisons.
-
Personalized Medicine and Treatment: By providing detailed anatomical information, labeled models can help tailor treatment strategies based on individual skin characteristics and conditions.
-
Drug Development and Testing: 3D skin models with accurate labeling serve as valuable tools for drug development and testing, allowing researchers to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new treatments in a controlled environment.
-
Cosmetics and Skin Care Innovation: Labeled models enable the development of more effective and targeted skincare products by providing insights into how different ingredients interact with skin structures.
Types of 3D Skin Models and Labeling Techniques:
The creation and labeling of 3D skin models involve a combination of advanced technologies and meticulous manual annotation. Here are some key approaches:
-
Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT): This technique uses X-rays to create detailed 3D images of skin samples, revealing the intricate network of cells, tissues, and structures.
-
Confocal Microscopy: Confocal microscopy allows researchers to visualize and label specific cellular components and structures by emitting laser light and capturing the emitted fluorescence.
-
Digital Reconstruction: Combining data from various imaging techniques and manual annotation, researchers can digitally reconstruct 3D models of skin, labeling different structures with specific colors or tags.
-
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These technologies enable immersive and interactive experiences with labeled 3D skin models, allowing users to explore the anatomy in a more engaging and intuitive manner.
FAQs about 3D Skin Models and Labeling:
Q1: What are the limitations of 3D skin models?
While 3D skin models offer significant advantages, they do have certain limitations. They are not perfect replicas of real skin and may not fully capture the dynamic nature of living tissue. Additionally, creating and labeling these models can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Q2: How can I access labeled 3D skin models for research purposes?
Several institutions, research groups, and commercial companies offer access to labeled 3D skin models for research purposes. These models are often available through online repositories or collaborations with researchers.
Q3: What are the future directions in 3D skin modeling and labeling?
Future advancements in 3D skin modeling are likely to focus on improving the realism and complexity of these models, incorporating dynamic features like cell movement and tissue growth. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a significant role in automating the labeling process, making these models more accessible and efficient.
Tips for Working with Labeled 3D Skin Models:
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define the specific research question or application you are addressing to choose the most appropriate model and labeling approach.
- Understand the Model’s Limitations: Be aware of the limitations of the model, such as the resolution and accuracy of the data.
- Utilize Available Software and Tools: Explore specialized software and tools for visualizing, analyzing, and manipulating labeled 3D skin models.
- Collaborate with Experts: Seek guidance from experts in 3D modeling, anatomy, and the specific research area you are investigating.
Conclusion:
Labeled 3D skin models are revolutionizing the field of dermatology and beyond. These powerful tools provide unprecedented insights into the intricacies of skin structure and function, facilitating groundbreaking research, personalized treatment, and innovative product development. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more realistic and sophisticated 3D skin models, further unlocking the secrets of this vital organ and advancing our understanding of human health.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: 3D Models and the Power of Labeling. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!